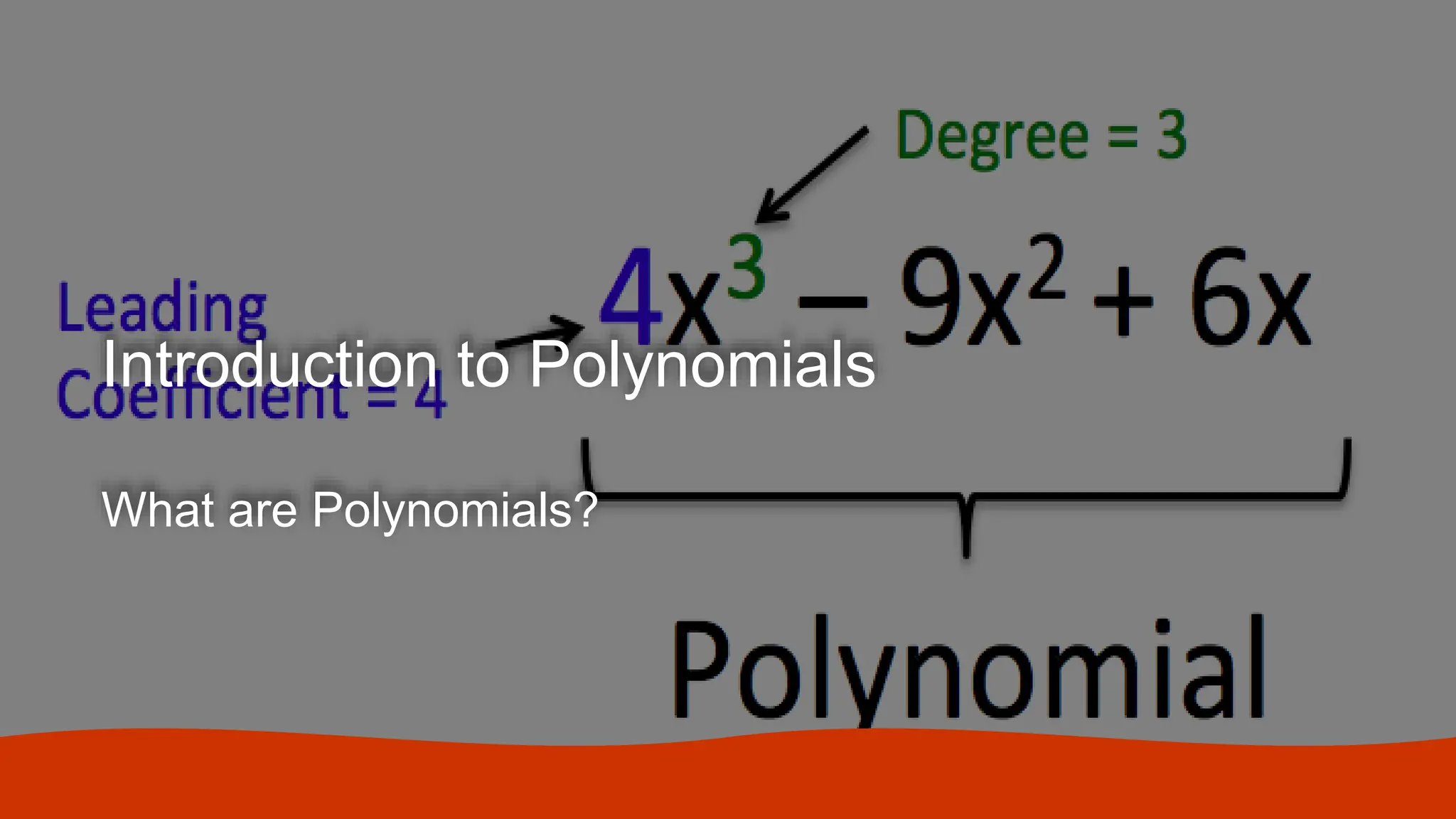
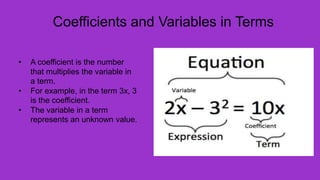
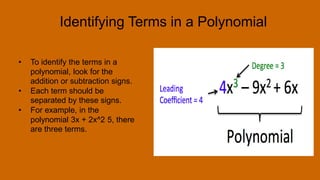
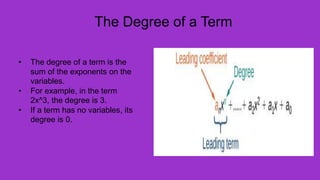
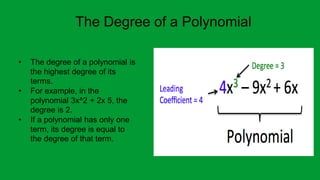
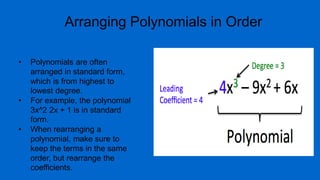
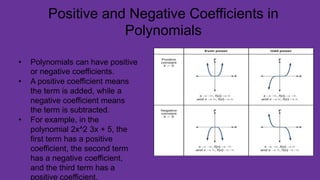
A polynomial is an algebraic expression made up of one or more terms combined using addition and subtraction. A term consists of a number called the coefficient multiplied by one or more variables raised to a non-negative integer power. The degree of a term is the sum of the exponents on the variables, and the degree of a polynomial is the highest degree among its terms. Polynomials can be classified based on the number of terms as monomials, binomials, trinomials, or polynomials with a degree greater than three.