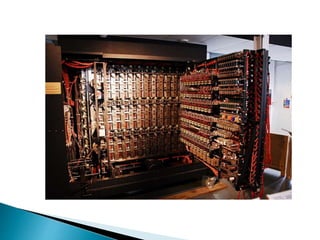
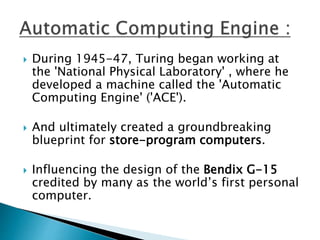
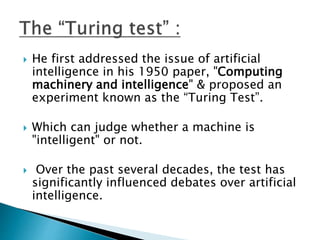
Alan Turing was a British mathematician who made pioneering contributions to computer science. During World War II, he worked at Bletchley Park cracking German codes transmitted by the Enigma machine. To help solve this problem faster than could be done by hand, Turing conceived of an electromechanical machine called the Bombe that could methodically search for potential code settings. Over 200 Bombes were built, allowing the Allies to decrypt thousands of messages per day and gain valuable intelligence. Turing's work is credited with shortening the war by as much as two years. He later did foundational work in computer science and artificial intelligence.