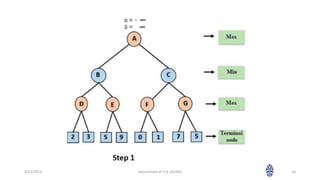
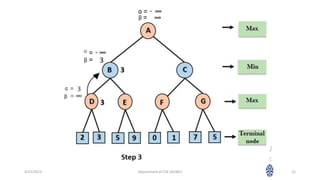
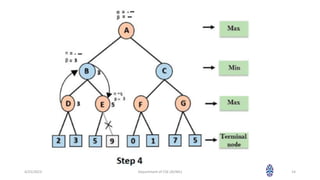
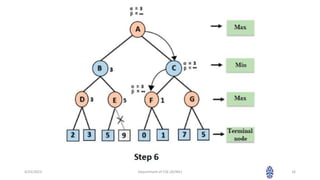
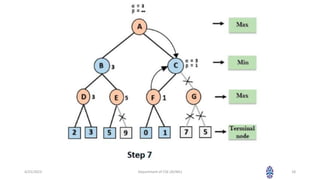
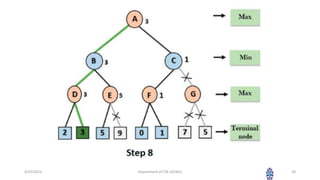
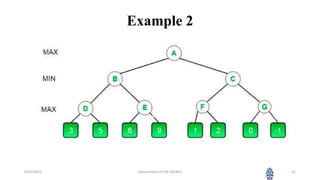
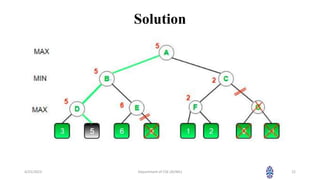
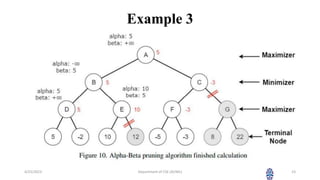
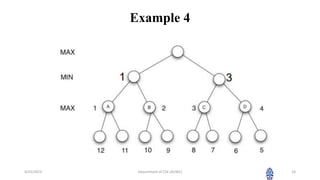
This document summarizes a session on artificial intelligence topics taught by Assistant Professor M. Gokilavani. The session covered adversarial search techniques like alpha-beta pruning which improves basic minimax search for game trees. Alpha-beta pruning uses threshold parameters alpha and beta to prune subtrees and avoid evaluating all game tree nodes. The document provides pseudocode for alpha-beta pruning and worked through an example of how it prunes a game tree by comparing node values to alpha and beta as it traverses the tree. Future sessions will cover additional topics like imperfect real-time decisions in games.