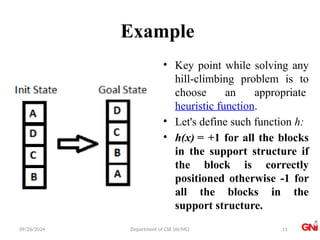
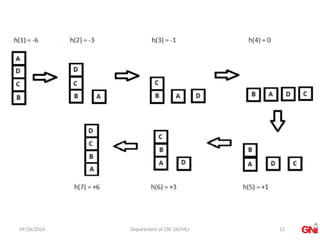
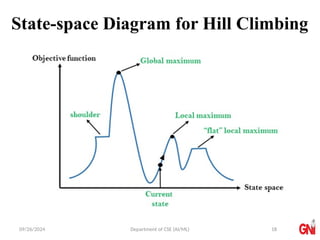
The document outlines a course on Artificial Intelligence, focusing on search algorithms and optimization methods, particularly the hill-climbing algorithm. It details various types of hill climbing, including simple, steepest-ascent, stochastic, and random-restart hill climbing, alongside the concept of simulated annealing. The document also explains the importance of heuristics and evaluation functions in navigating search spaces effectively.