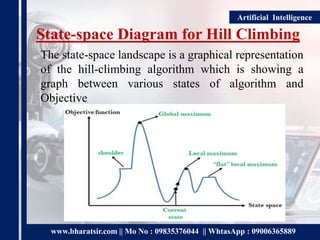
The document discusses the hill-climbing algorithm in artificial intelligence, which optimizes mathematical problems by continually moving towards peak solutions without backtracking. It outlines different types of hill climbing algorithms, including simple, steepest-ascent, and stochastic variations, along with their advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Key features include generating and testing variants, a greedy approach to searching, and the use of state-space diagrams to visualize the algorithm's landscape.