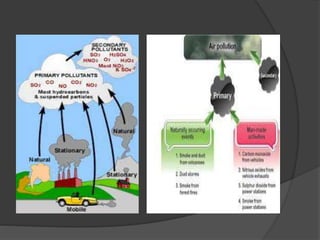
The document provides a comprehensive overview of air pollution, defining it as the presence of harmful substances in the air. It categorizes air pollutants into primary and secondary types and discusses their sources, effects on human health, animals, plants, materials, and climate. Additionally, it outlines methods for controlling air pollution including the use of trees, emissions reduction, and various filtration technologies.

















![REFERENCE
S. Deswal, A. Deswal; “A basic course in
Environmental studies” Second revised edition,
Reprint:(2013) New delhi. Dhanpat Rai & CO. (P)
LTD. Education and technical publioshers. Page
5.2-5.3
Health effects of outdoor air pollution. Committee
of the Environmental and Occupational Health
Assembly of the American Thoracic Society.
(1996). [Comparative Study Review]. American
journal of respiratory and critical care medicine,
153(1), 3-50.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airpollution-150408115822-conversion-gate01/85/Air-pollution-source-effect-and-cont-19-320.jpg)
