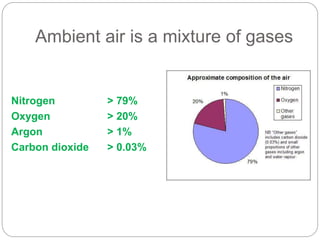
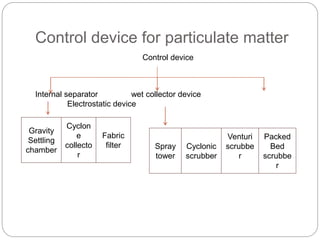
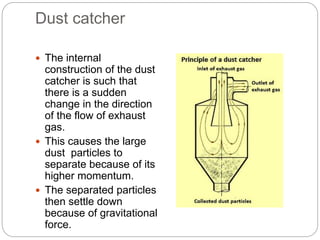
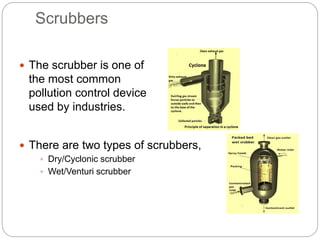
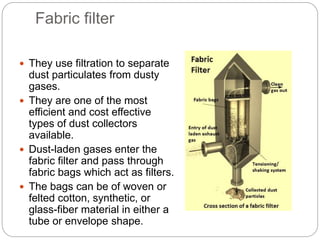
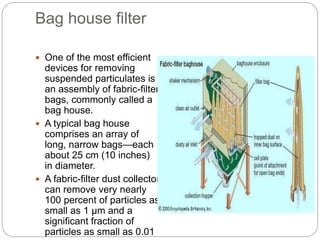
This document presents an overview of different air pollution filtering techniques. It begins with introducing air composition and sources of air pollution. Then it discusses various control devices for particulate matter removal, including internal separator wet collectors, electrostatic precipitators, gravity settlers, cyclones, spray towers, cyclonic scrubbers, packed bed scrubbers, and venturi scrubbers. Further techniques covered are filtration devices like dust catchers, dry and wet scrubbers, fabric filters, electrostatic precipitators, air ventilation, bag house filters, and flue gas desulfurization. Specific operating mechanisms are described for dust catchers, scrubbers, fabric filters, electrostatic precipitators, air ventilation, bag house filters, and flue