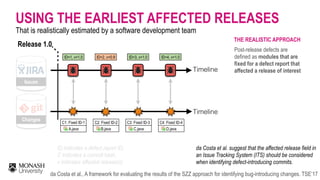
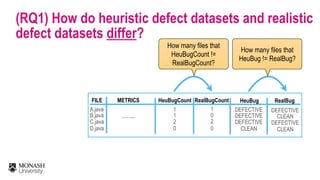
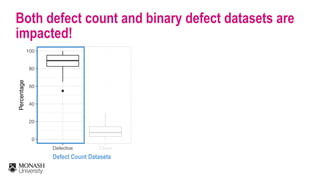
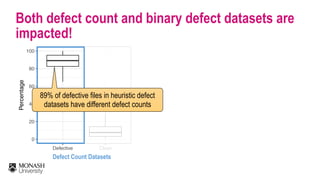
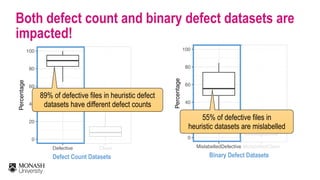
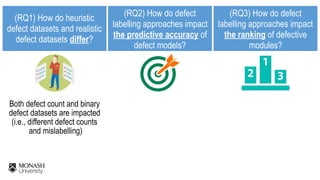
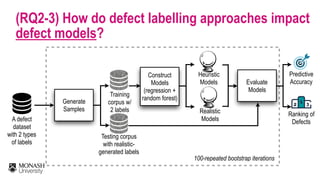
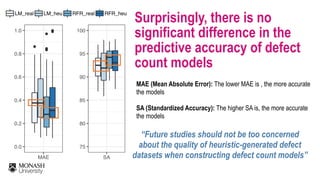
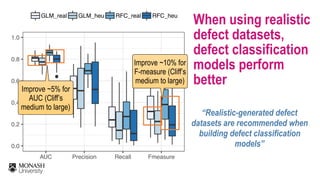
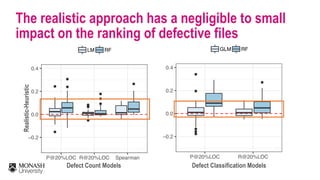
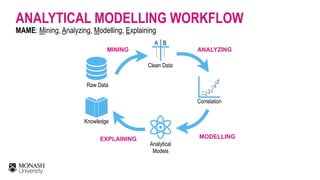
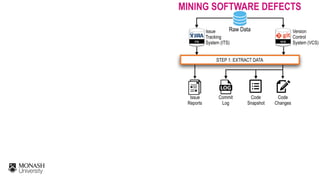
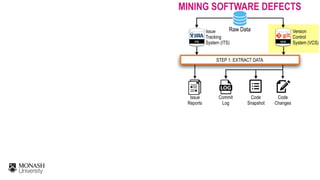
The document discusses analytical models for predicting software defects and the challenges of mining software defects, particularly focusing on the definition and identification of post-release defects. It emphasizes the importance of data extraction from issue tracking systems and version control repositories to effectively analyze software quality and provide insights for managerial decision-making. Additionally, it contrasts heuristic and realistic approaches to defect labeling, highlighting the impact on predictive accuracy and ranking of defective modules.



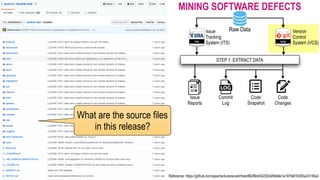
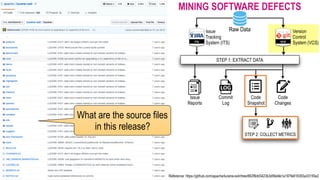
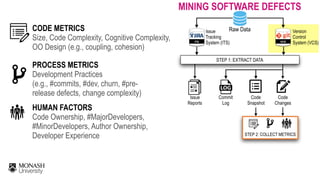
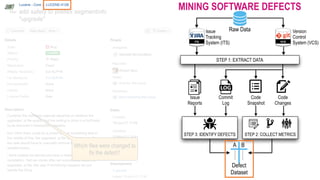
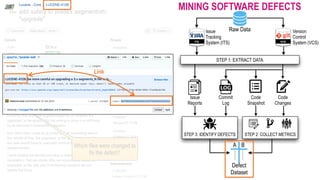
![CHALLENGES OF MINING SOFTWARE DEFECTS
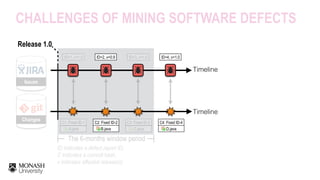
THE HEURISTIC APPROACH
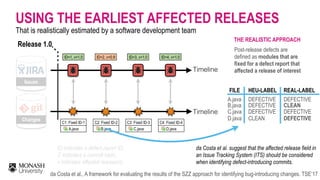
Post-release defects are
defined as modules that are
fixed for a defect report
within a post-release window
period (e.g., 6 months)
[Fischer et al, ICSM’03]
ID indicates a defect report ID,
C indicates a commit hash,
v indicates affected release(s)
Release 1.0
Changes
Issues
Timeline
Timeline
Fischer et al., “Populating a Release History Database from Version Control and Bug Tracking Systems”, ICSM’03](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icse2019-mining-software-defects-190531160651/85/Mining-Software-Defects-Should-We-Consider-Affected-Releases-23-320.jpg)
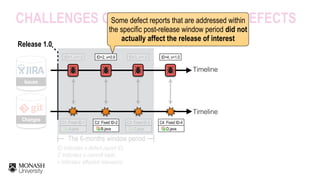
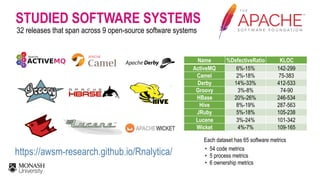
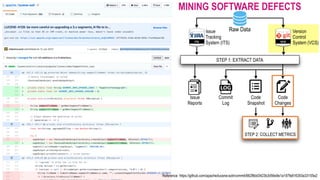
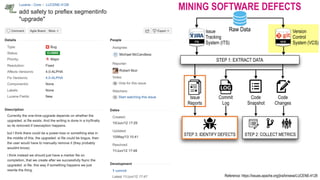
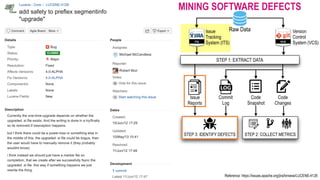
![The 6-months window period
CHALLENGES OF MINING SOFTWARE DEFECTS
THE HEURISTIC APPROACH
Post-release defects are
defined as modules that are
fixed for a defect report
within a post-release window
period (e.g., 6 months)
[Fischer et al, ICSM’03]
ID indicates a defect report ID,
C indicates a commit hash,
v indicates affected release(s)
Release 1.0
Changes
Issues
Timeline
Timeline
C1: Fixed ID-1
ID=1, v=1.0
A.java
ID=2, v=0.9
C2: Fixed ID-2
B.java
ID=3, v=1.0
C3: Fixed ID-3
C.java
ID=4, v=1.0
C4: Fixed ID-4
D.java
Fischer et al., “Populating a Release History Database from Version Control and Bug Tracking Systems”, ICSM’03](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icse2019-mining-software-defects-190531160651/85/Mining-Software-Defects-Should-We-Consider-Affected-Releases-24-320.jpg)
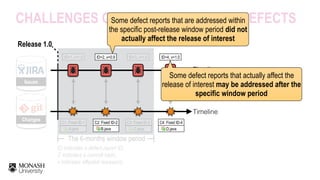
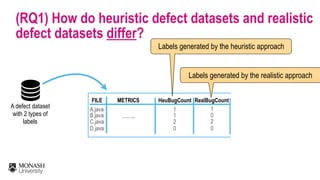
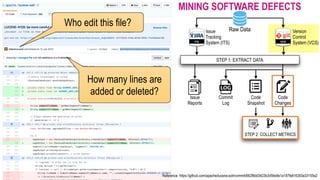
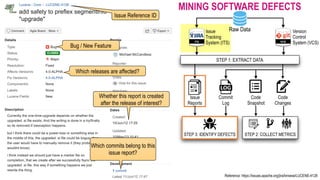
![The 6-months window period
CHALLENGES OF MINING SOFTWARE DEFECTS
FILE HEU-LABEL
DEFECTIVE
DEFECTIVE
DEFECTIVE
CLEAN
A.java
B.java
C.java
D.java
THE HEURISTIC APPROACH
Post-release defects are
defined as modules that are
fixed for a defect report
within a post-release window
period (e.g., 6 months)
[Fischer et al, ICSM’03]
ID indicates a defect report ID,
C indicates a commit hash,
v indicates affected release(s)
Release 1.0
Changes
Issues
Timeline
Timeline
C1: Fixed ID-1
ID=1, v=1.0
A.java
ID=2, v=0.9
C2: Fixed ID-2
B.java
ID=3, v=1.0
C3: Fixed ID-3
C.java
ID=4, v=1.0
C4: Fixed ID-4
D.java
Fischer et al., “Populating a Release History Database from Version Control and Bug Tracking Systems”, ICSM’03](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icse2019-mining-software-defects-190531160651/85/Mining-Software-Defects-Should-We-Consider-Affected-Releases-25-320.jpg)