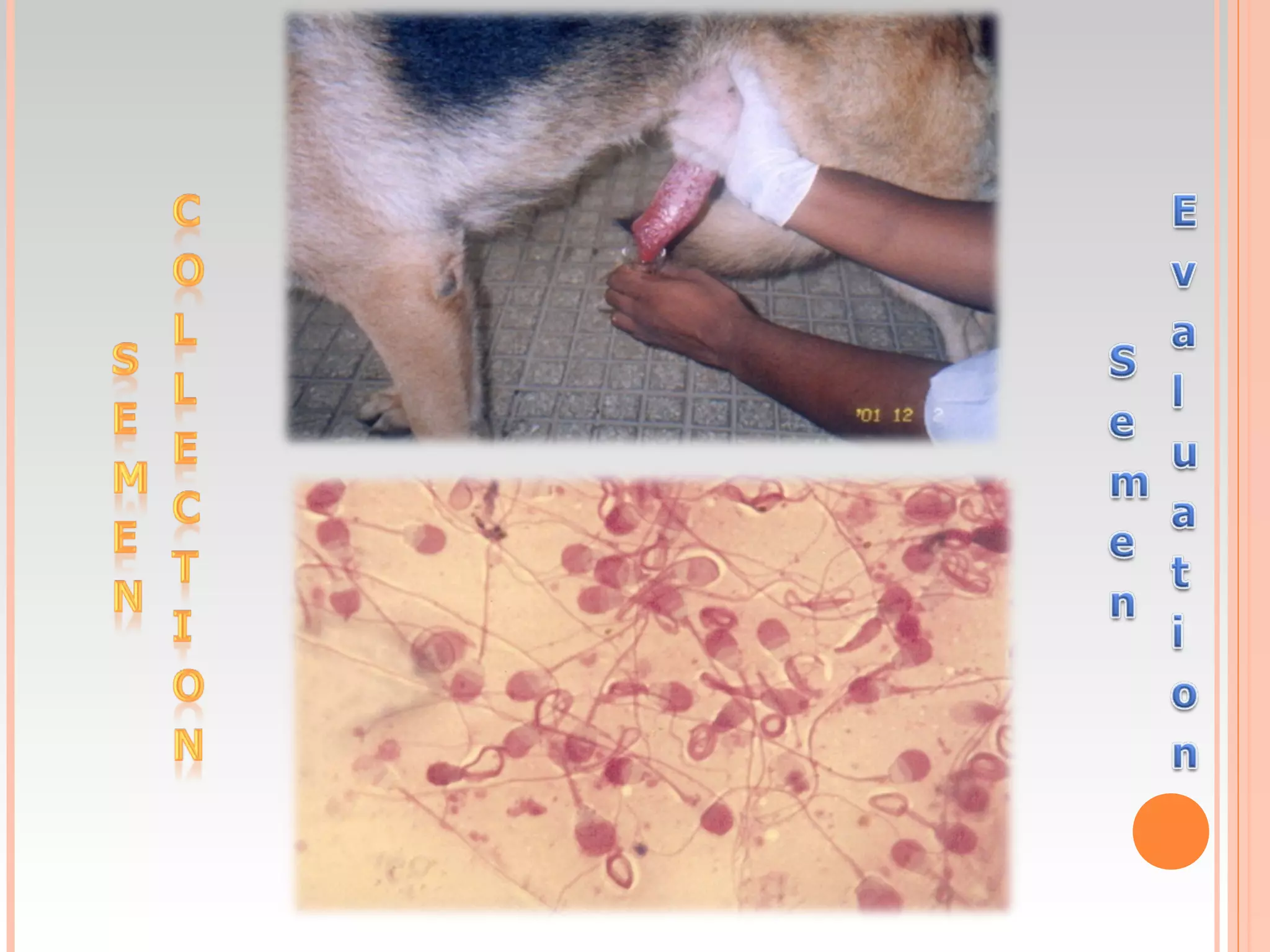
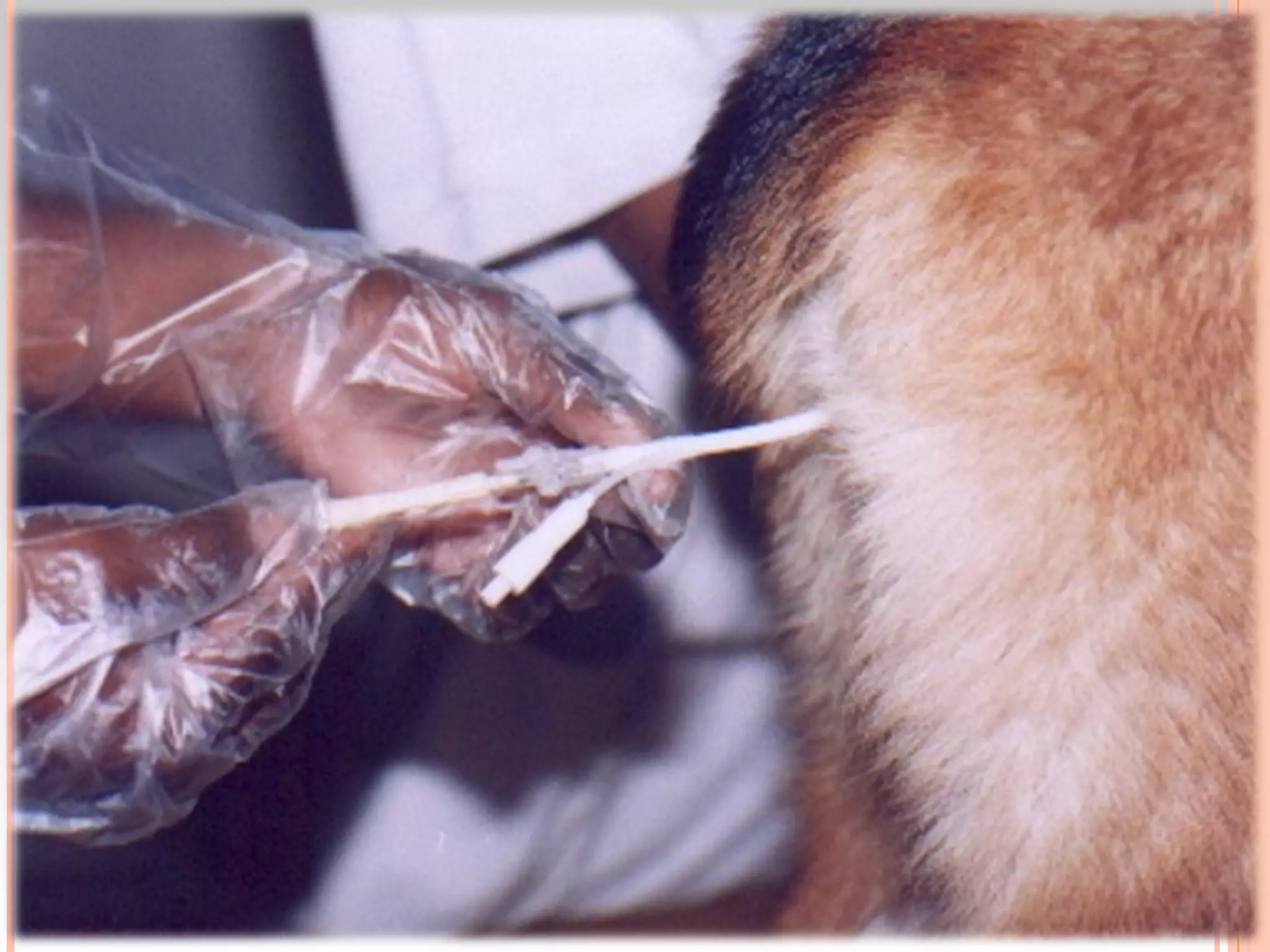
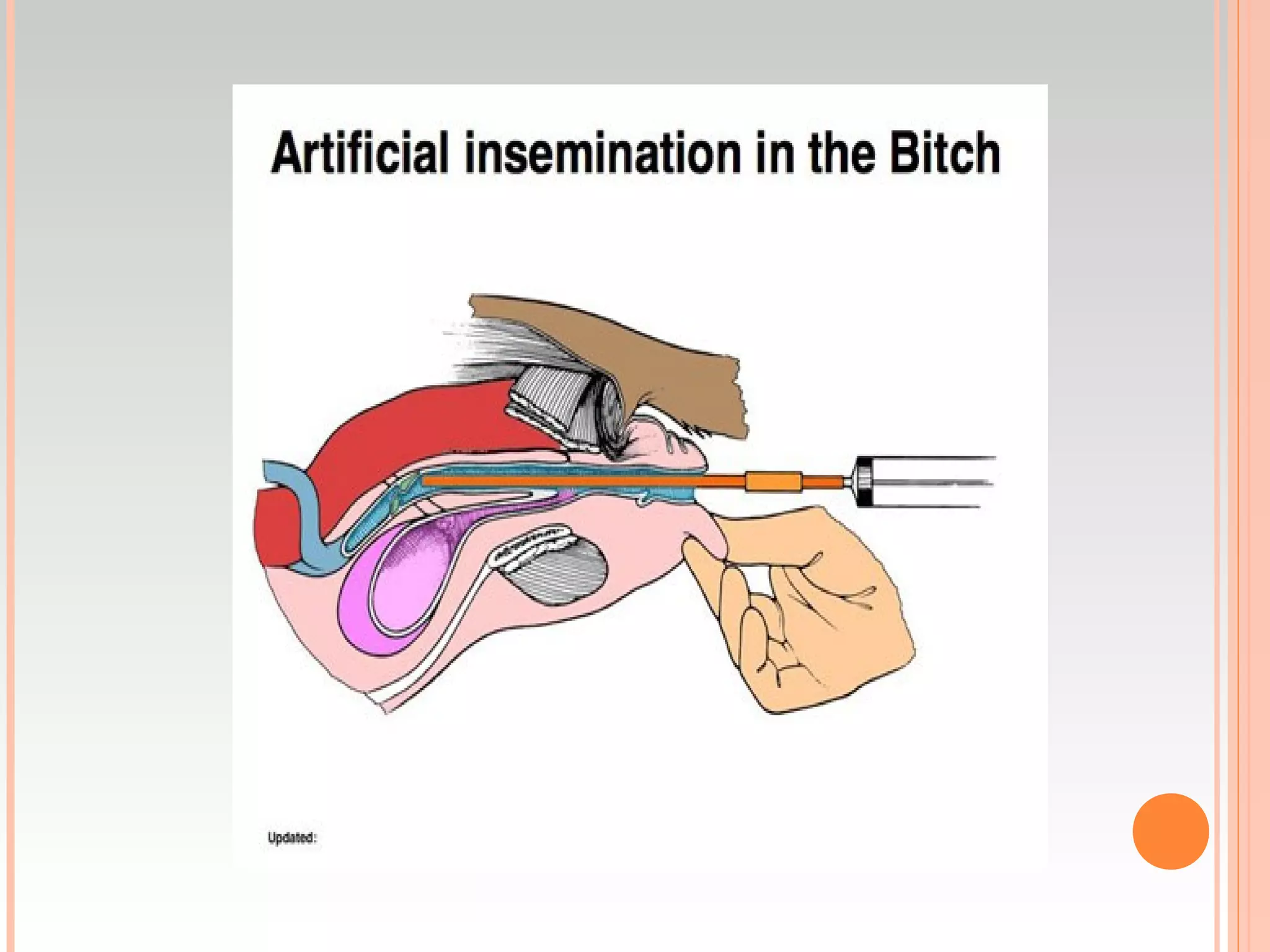
Artificial insemination and ultrasound are effective methods for diagnosing pregnancy in bitches. Ultrasound can confirm pregnancy as early as 24-25 days and is 99% accurate at 28 days by visualizing the amniotic vesicle and fetal heartbeat. Radiography is 100% accurate in the last 15 days by seeing mineralized fetal bones. Hormonal assays of relaxin and acute phase proteins after 20 days also reliably indicate pregnancy.