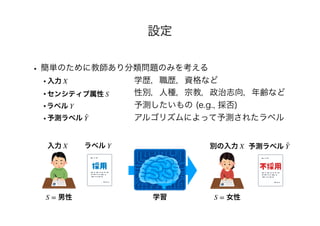
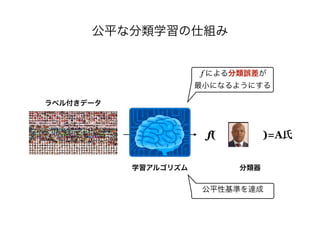
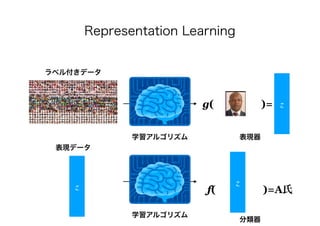
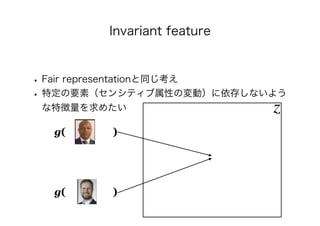
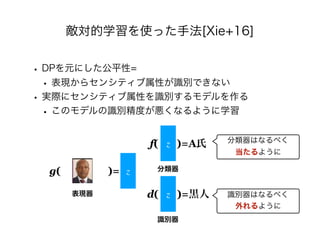
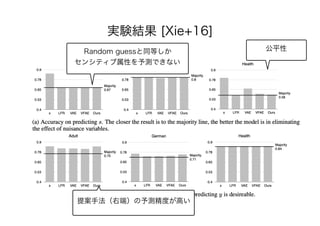
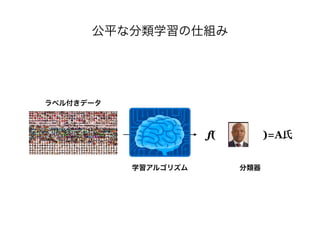
- The document discusses several papers related to algorithmic fairness in machine learning. It summarizes papers that propose definitions of fairness, present algorithms for learning fair representations and classifiers, and analyze fairness in contextual settings like bandits and reinforcement learning.
- The summaries cover work on ensuring equality of opportunity, calibration, awareness-based fairness, reduction-based approaches, learning fair representations without adversarial training, and analyzing fairness in online and sequential decision making problems.
- Concerns about potential issues like inherent tradeoffs in fairness, fairwashing by rationalization, and faking fairness through sampling biases are also mentioned.








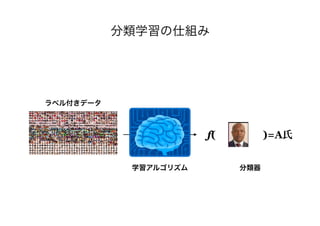
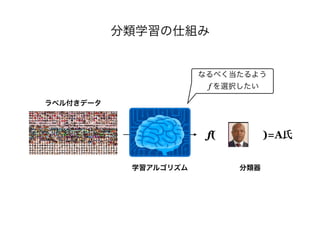
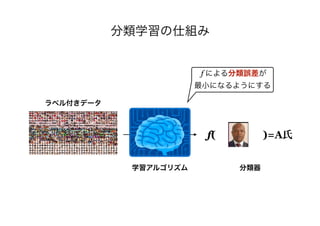
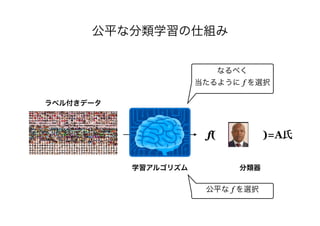
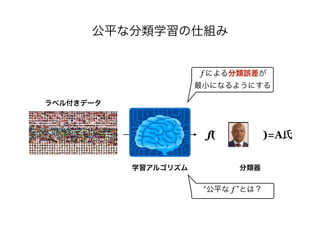




![Q
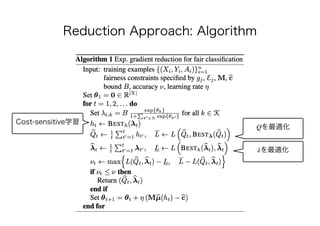
Q f
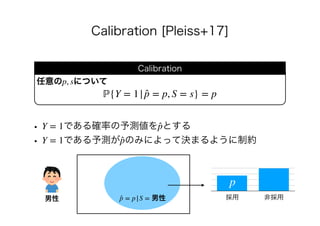
minQ 𝔼f∼Qℙ{f(X) ≠ Y} M𝔼f∼Q[μ(f )] ≤ c
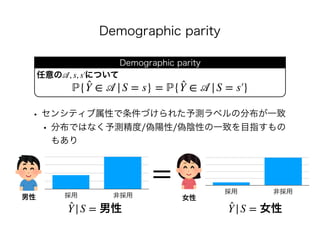
𝔼{f(X)|S = 0} = 𝔼{f(X)}
𝔼{f(X)|S = 1} = 𝔼{f(X)}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-23-320.jpg)
![minQ 𝔼f∼Qℙ{f(X) ≠ Y} M𝔼f∼Q[μ(f )] ≤ c
maxλ∈ℝK
+,∥λ∥≤B minQ 𝔼f∼Qℙ{f(X) ≠ Y} + λ⊤
(M𝔼f∼Q[μ(f )] − c)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-24-320.jpg)






![minθ 𝔼[ℓ0(X, θ)] 𝔼[ℓi(X, θ)] ≤ 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-46-320.jpg)


![̂Y = 1 h : 𝒳 → [0,1]
h ℓ0
ℙx,x′{|h(x) − h(x′)| > d(x, x′) + γ} ≤ α
(γ, α)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-50-320.jpg)













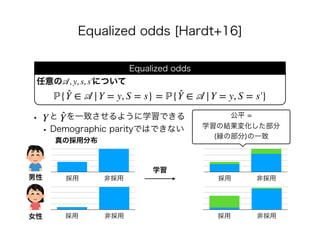
![• [Hardt+16] Moritz Hardt, Eric Price, and Nathan Srebro.
Equality of Opportunity in Supervised Learning. In: NeurIPS,
pp. 3315-3323, 2016. https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02413
• [Pleiss+17] Geoff Pleiss, Manish Raghavan, Felix Wu, Jon
Kleinberg, and Kilian Q. Weinberger. On Fairness and
Calibration. In: NeurIPS, pp. 5680-5689, 2017. https://arxiv.org/
abs/1709.02012
• [Dwork+12] Cynthia Dwork, Moritz Hardt, Toniann
Pitassi, Omer Reingold, Rich Zemel. Fairness Through
Awareness. In: the 3rd innovations in theoretical computer
science conference, pp. 214-226, 2012. https://arxiv.org/abs/
1104.3913](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-71-320.jpg)
![• [Agarwal+18] Alekh Agarwal, Alina Beygelzimer, Miroslav
Dudík, John Langford, and Hanna Wallach. A Reductions
Approach to Fair Classification. In: ICML, PMLR 80, pp.
60-69, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.02453
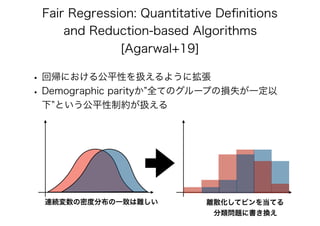
• [Agarwal+19] Alekh Agarwal, Miroslav Dudík, and Zhiwei
Steven Wu. Fair Regression: Quantitative Definitions and
Reduction-based Algorithms. In: ICML, PMLR 97, pp. 120-129,
2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.12843
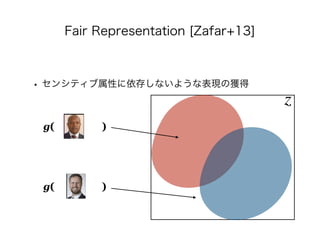
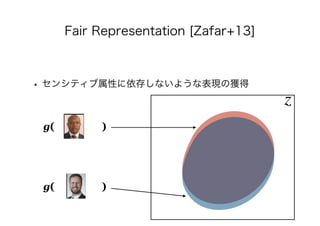
• [Zafar+13] Rich Zemel, Yu Wu, Kevin Swersky, Toni Pitassi,
and Cynthia Dwork. Learning Fair Representations. In: ICML,
PMLR 28, pp. 325-333, 2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-72-320.jpg)
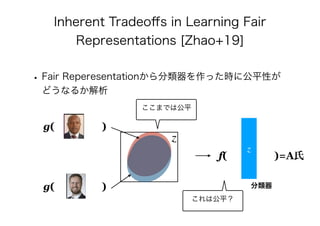
![• [Zhao+19] Han Zhao, Geoffrey J. Gordon. Inherent Tradeoffs in
Learning Fair Representations. In: NeurIPS, 2019, to appear.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08386
• [Xie+16] Qizhe Xie, Zihang Dai, Yulun Du, Eduard
Hovy, Graham Neubig. Controllable Invariance through
Adversarial Feature Learning. In: NeurIPS, pp. 585-596, 2016.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.11122
• [Moyer+18] Daniel Moyer, Shuyang Gao, Rob
Brekelmans, Greg Ver Steeg, and Aram Galstyan. Invariant
Representations without Adversarial Training. In: NeurIPS, pp.
9084-9893, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.09458](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-73-320.jpg)
![• [Woodworth+18] Blake Woodworth, Suriya Gunasekar, Mesrob
I. Ohannessian, Nathan Srebro. Learning Non-Discriminatory
Predictors. In: COLT, pp. 1920-1953, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/
1702.06081
• [Cotter+19] Andrew Cotter, Maya Gupta, Heinrich
Jiang, Nathan Srebro, Karthik Sridharan, Serena Wang, Blake
Woodworth, Seungil You. Training Well-Generalizing
Classifiers for Fairness Metrics and Other Data-Dependent
Constraints. In: ICML, PMLR 97, pp. 1397-1405, 2019. https://
arxiv.org/abs/1807.00028
• [Rothblum+18] Guy N. Rothblum, Gal Yona. Probably
Approximately Metric-Fair Learning. In: ICML, PMLR 80, pp.
5680-5688, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.03242](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-74-320.jpg)
![• [Joseph+16] Matthew Joseph, Michael Kearns, Jamie
Morgenstern, Aaron Roth. Fairness in Learning: Classic and
Contextual Bandits. In: NeurIPS, pp. 325-333, 2016.
• [Liu+17] Yang Liu, Goran Radanovic, Christos
Dimitrakakis, Debmalya Mandal, David C. Parkes. Calibrated
Fairness in Bandits. In: 4th Workshop on Fairness,
Accountability, and Transparency in Machine Learning
(FATML), 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01875
• [Gillen+18] Stephen Gillen, Christopher Jung, Michael
Kearns, Aaron Roth. Online Learning with an Unknown
Fairness Metric. In: NeurIPS, pp. 2600-2609, 2018. https://
arxiv.org/abs/1802.06936](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-75-320.jpg)
![• [Jabbari+17] Shahin Jabbari, Matthew Joseph, Michael Kearns, Jamie
Morgenstern, Aaron Roth. Fairness in Reinforcement Learning. In:
ICML, PMLR 70, pp. 1617-1626, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.03071
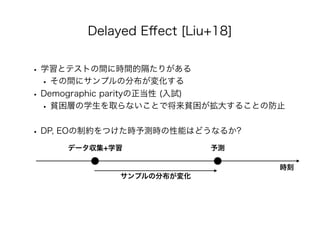
• [Liu+18] Lydia T. Liu, Sarah Dean, Esther Rolf, Max
Simchowitz, Moritz Hardt. Delayed Impact of Fair Machine Learning.
In: ICML, PMLR 80, pp. 3150-3158, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/
1803.04383
• [Aivodji+19] Ulrich Aïvodji, Hiromi Arai, Olivier Fortineau, Sébastien
Gambs, Satoshi Hara, Alain Tapp. Fairwashing: the risk of
rationalization. In: ICML, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.09749
• [Fukuchi+20] Kazuto Fukuchi, Satoshi Hara, Takanori Maehara. Faking
Fairness via Stealthily Biased Sampling. In: AAAI, Special Track on AI
for Social Impact (AISI), 2020, to appear. https://arxiv.org/abs/
1901.08291](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/present-191126093741/85/AI-76-320.jpg)






















