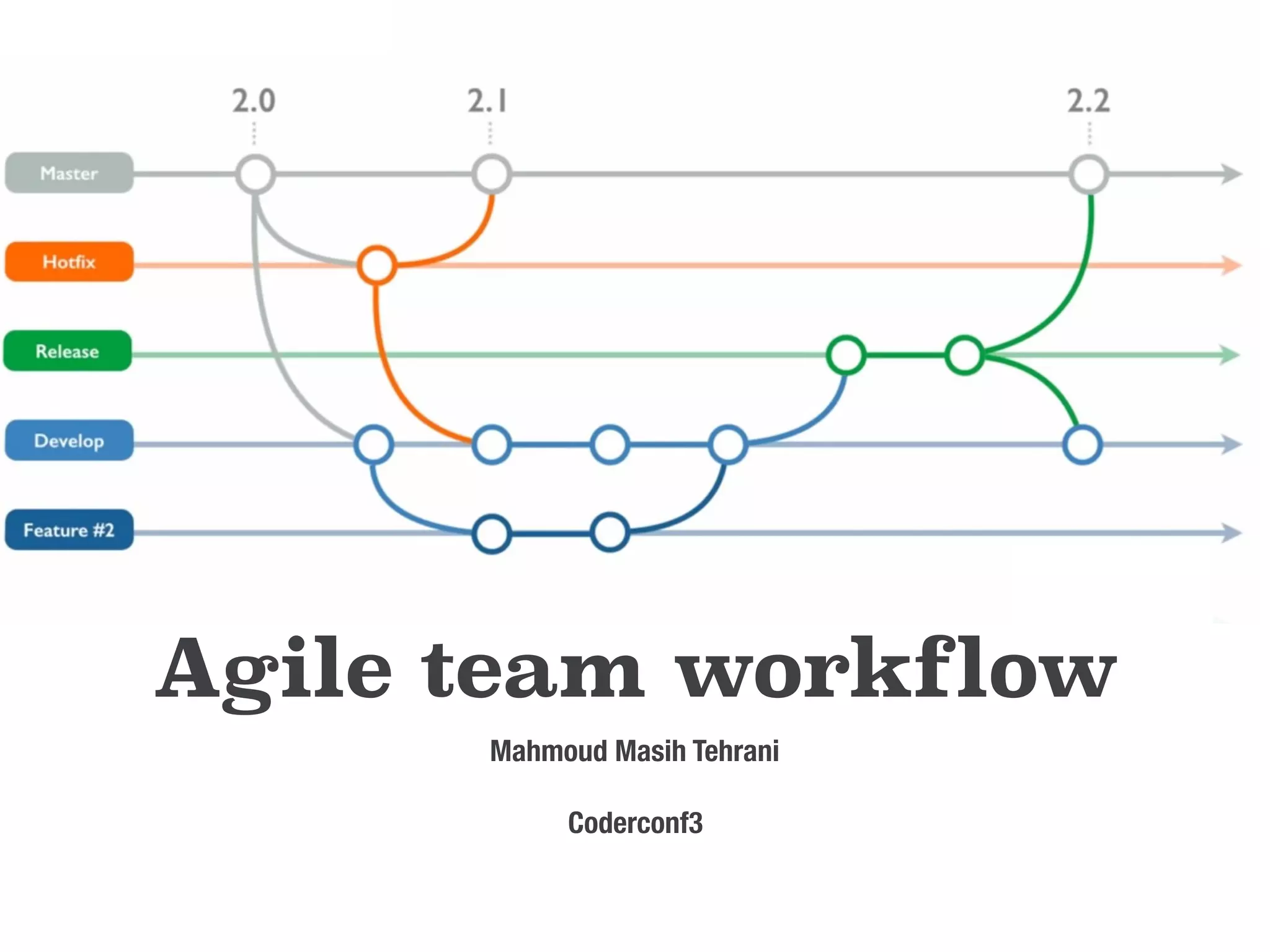
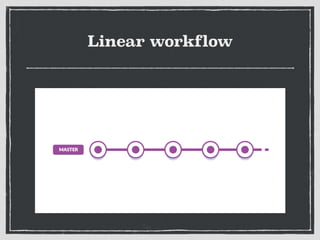
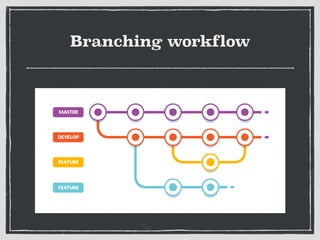
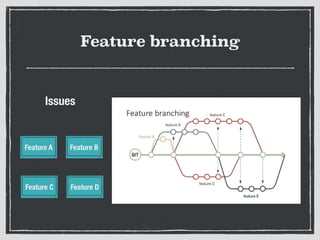
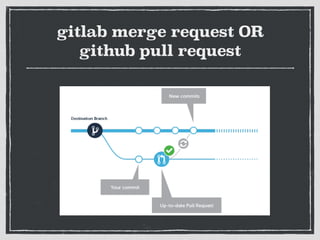
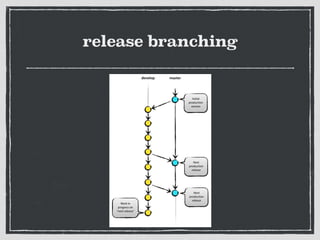
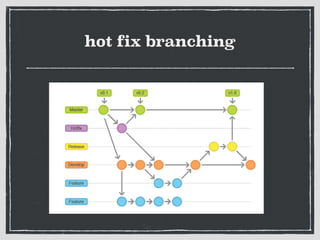
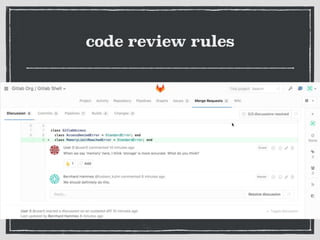
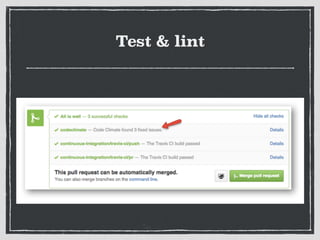
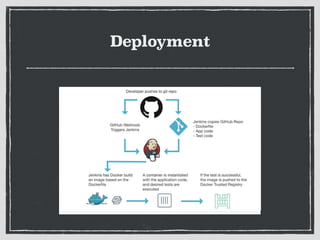
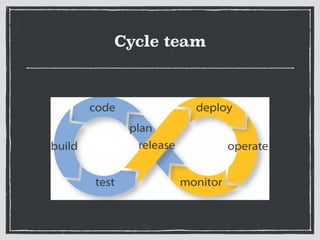
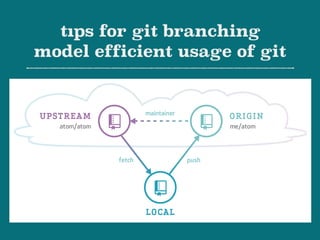
The document provides an overview of Git, a distributed version control system created by Linus Torvalds, including its benefits and common misconceptions about its complexity. It discusses various Git workflows, branching models, best practices for code commits, and the importance of code review and testing. Additionally, it emphasizes effective usage tips and resources for learning Git.