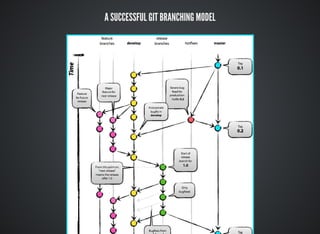
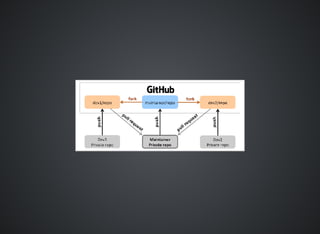
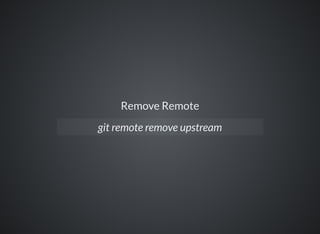
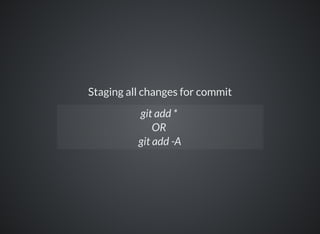
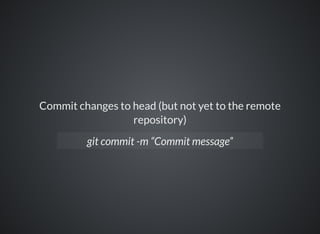
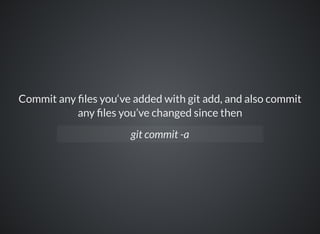
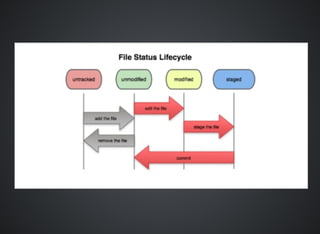
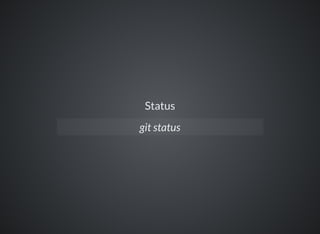
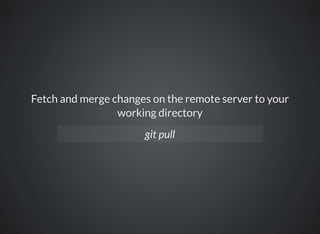
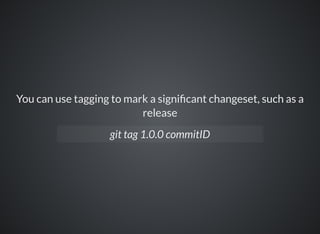
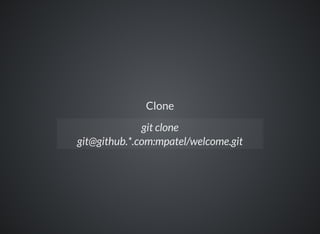
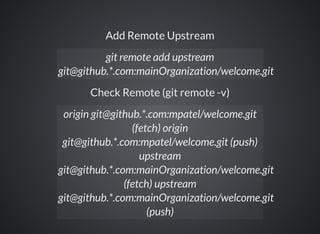
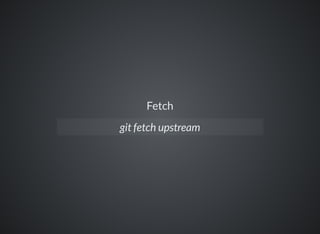
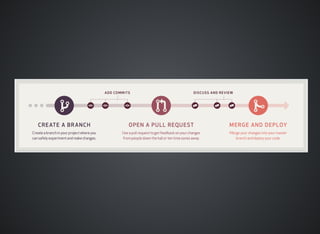
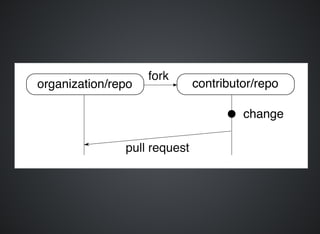
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Git, covering its advantages in version control such as performance, flexibility, and security features. It discusses various workflows for teams, including centralized and feature branch models, along with commands for repository management, branching, and merging. Best practices and additional resources for using Git effectively are also outlined.