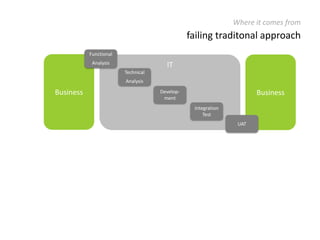
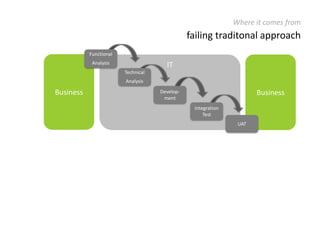
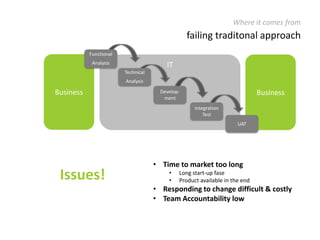
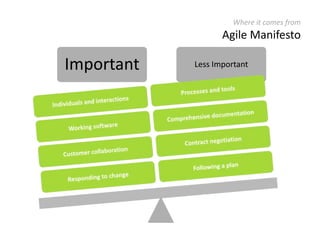
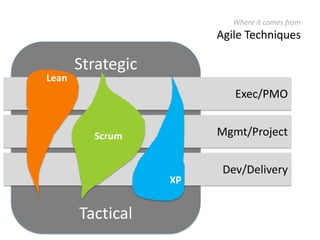
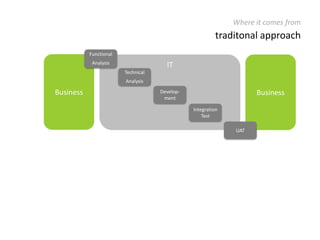
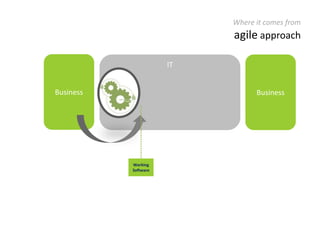
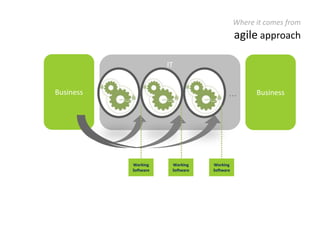
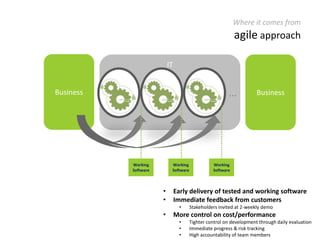
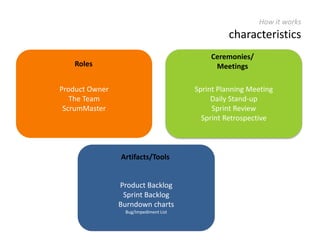
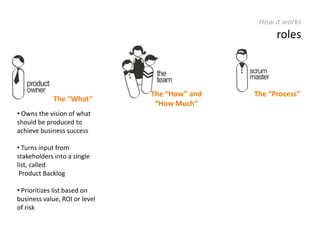
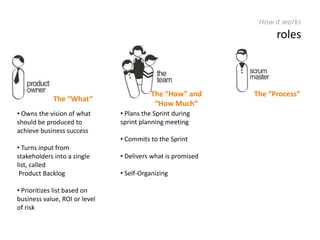
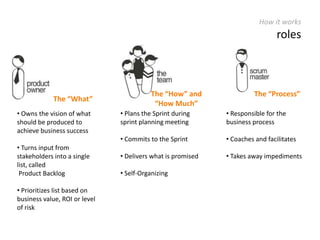
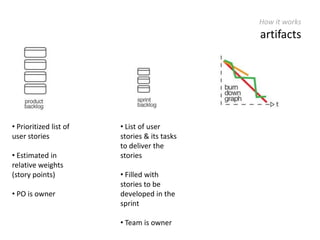
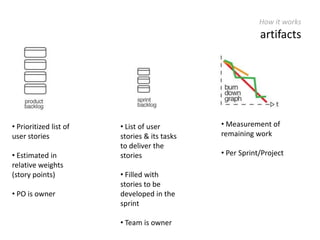
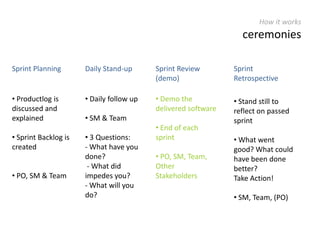
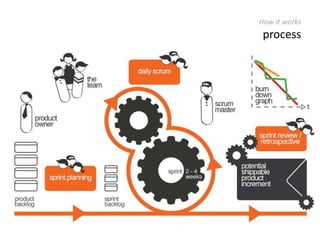
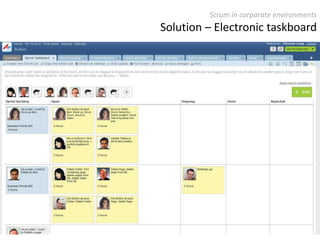
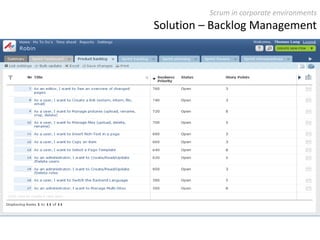
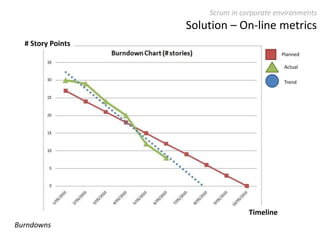
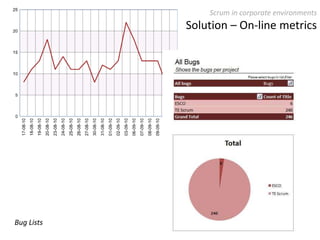
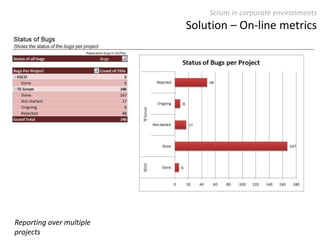
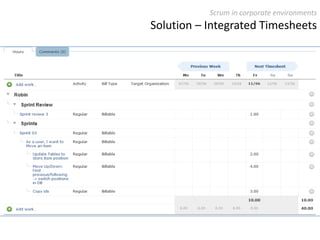
The document provides an overview of Scrum, an iterative framework for agile project management that enhances transparency, accountability, and speed in software development. It outlines key benefits, roles, ceremonies, and artifacts associated with Scrum, emphasizing its ability to deliver higher quality results while accommodating changing customer needs. Additionally, it discusses challenges in corporate environments and presents solutions, including the use of a pragmatic tool, PMScrum, to support distributed teams and multiple projects.