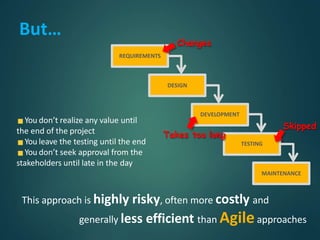
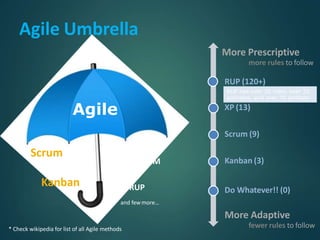
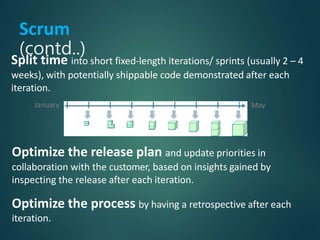
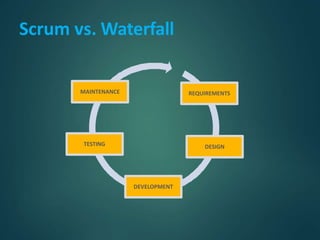
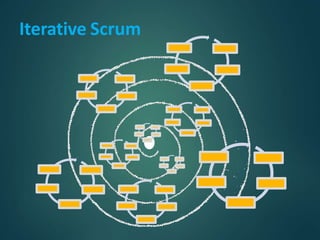
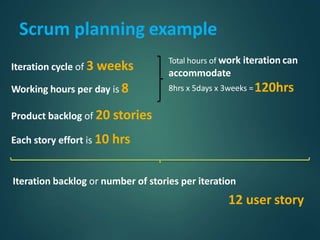
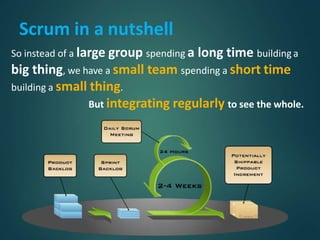
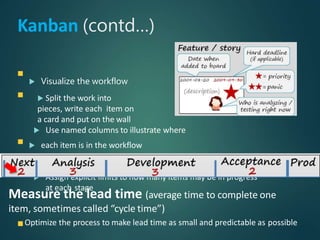
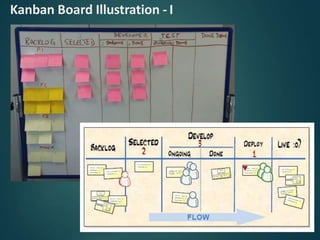
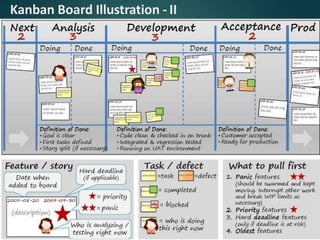
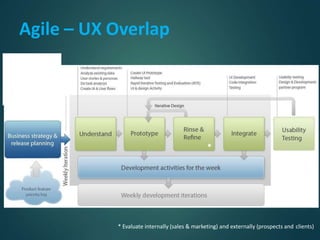
This document provides an overview of agile methodology and compares it to traditional waterfall development. It describes that agile focuses on iterative development with working software delivered frequently in short cycles. The key principles of the agile manifesto are also outlined. Specific agile frameworks like Scrum and Kanban are then explained in more detail. Scrum uses sprints, daily stand-ups, and artifacts like backlogs and burn-down charts. Kanban emphasizes visualizing and limiting work in progress to optimize flow. UX design is noted as an area that can benefit from adopting agile principles.
![Overview of
Agile Methodology
Dhruv Kumar [Mercer : Correspondence Team]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agilemethodology-200427064019/75/Agile-methodology-1-2048.jpg)
![A [really] short history of
Software development processes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agilemethodology-200427064019/85/Agile-methodology-2-320.jpg)