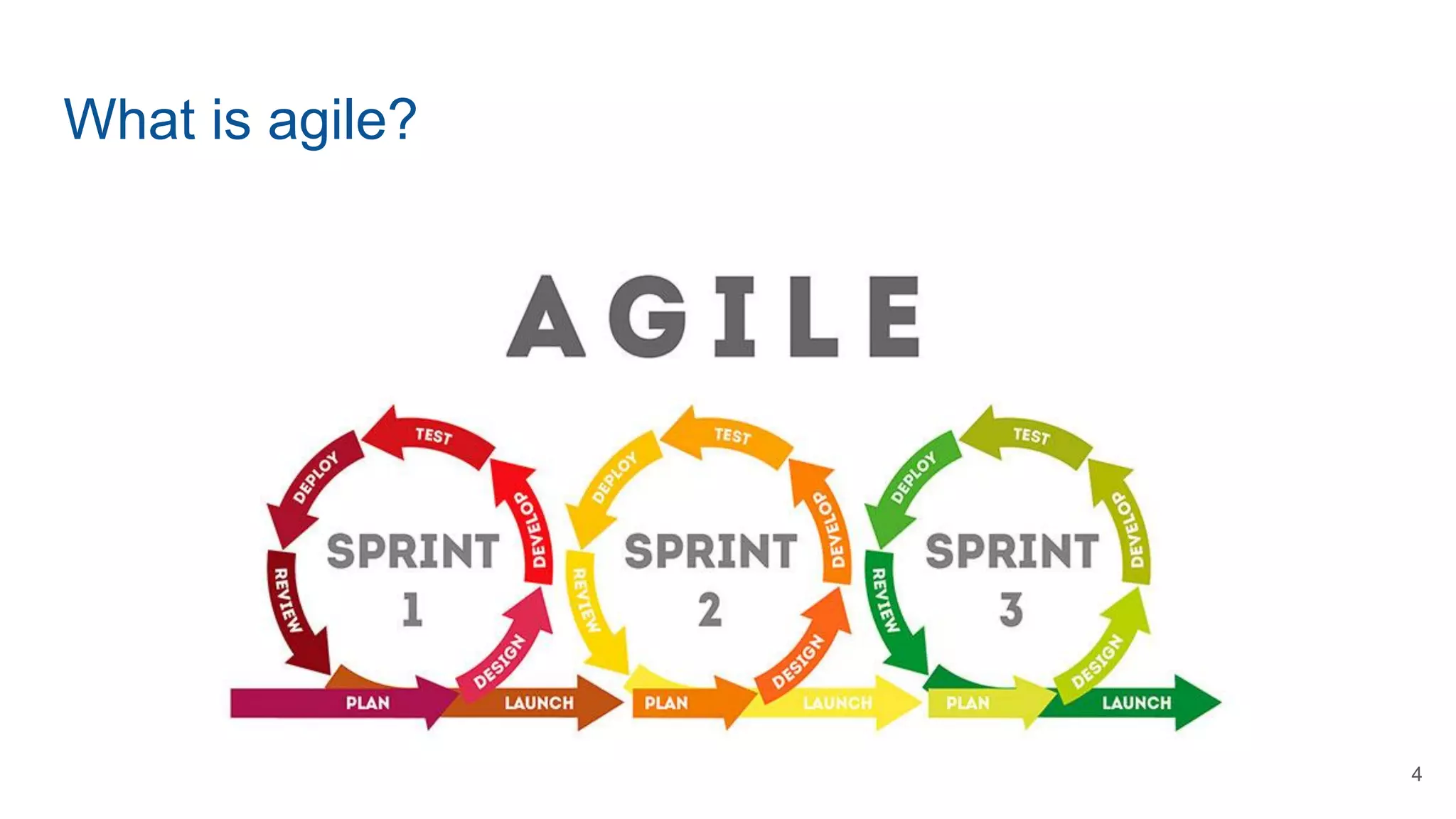
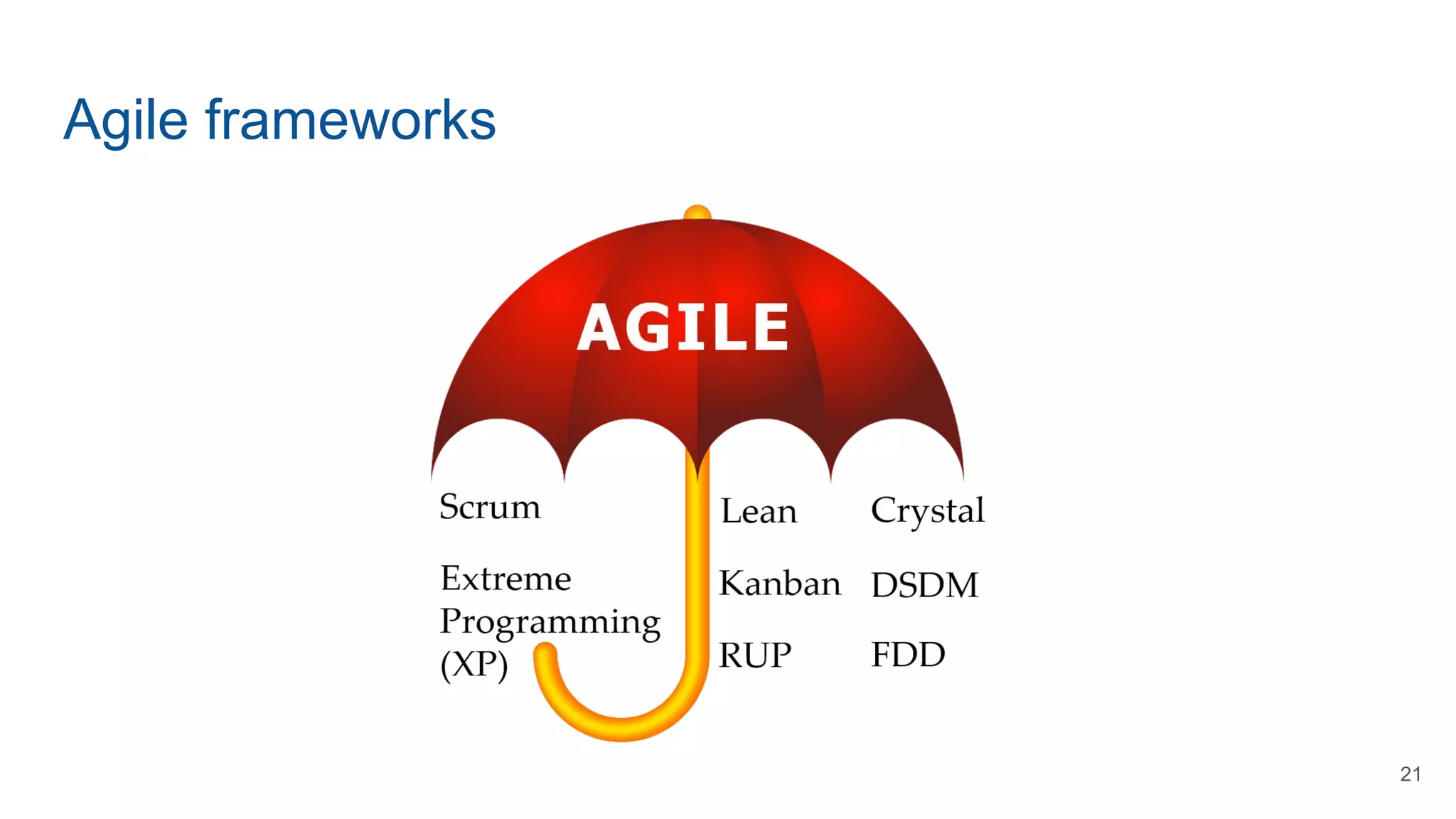
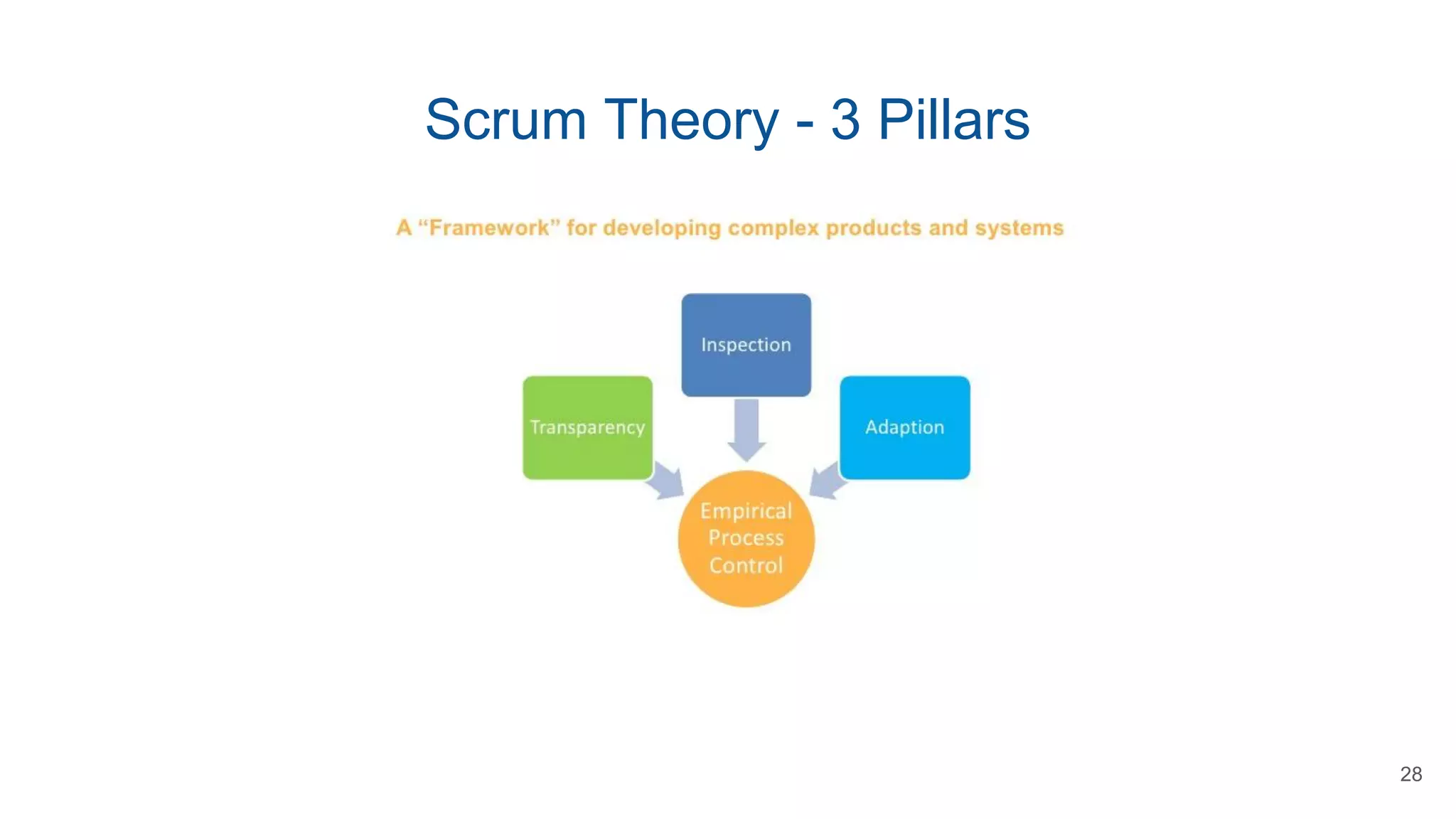
This document provides an overview of Scrum methodology for certification exam preparation, detailing its principles, roles, and framework. It outlines the Agile approach, emphasizing collaboration, customer satisfaction, and adaptability, and explains key Scrum components including events and artifacts. Additionally, the document offers exam tips and definitions to aid understanding of Scrum practices.