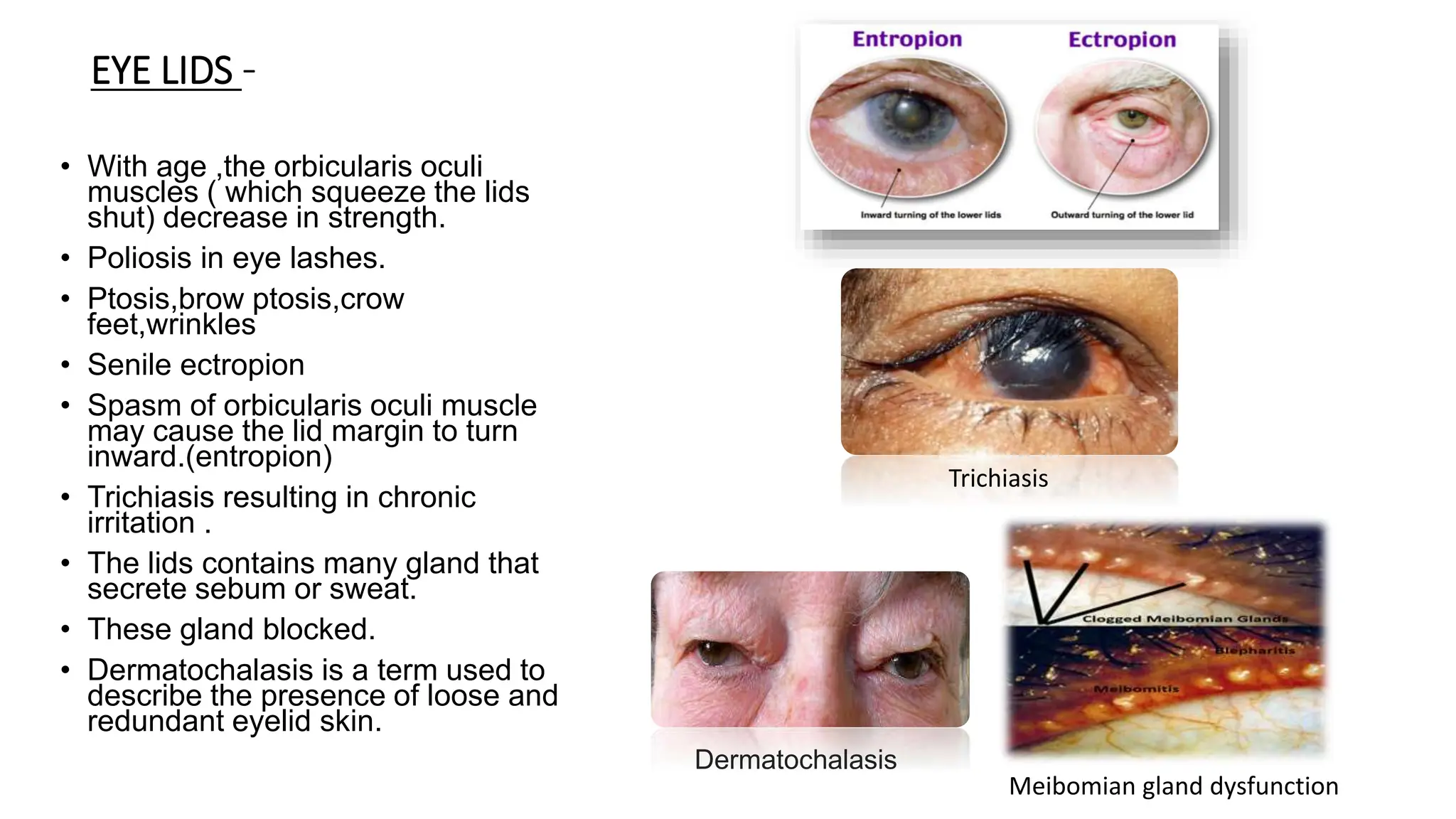
The document outlines the various age-related changes in the eye, affecting structures such as the eyelids, lacrimal glands, sclera, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, crystalline lens, vitreous humor, and retina. These changes lead to conditions like cataracts, dry eyes, reduced tear production, and age-related macular degeneration, resulting in diminished visual acuity and comfort. The document details specific physical changes in the eye and their implications for vision in the elderly.