The document discusses population and development from a historical and theoretical perspective. It makes three key points:
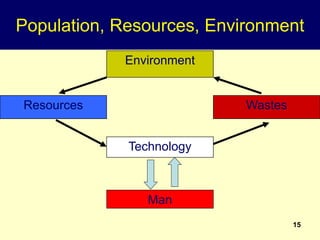
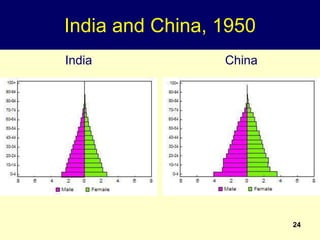
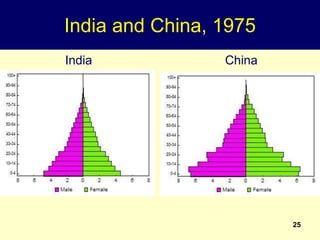
1. All development is for the benefit of people, and population characteristics like size, age, and sex determine development needs. Development also modifies population factors.
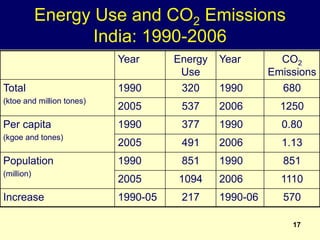
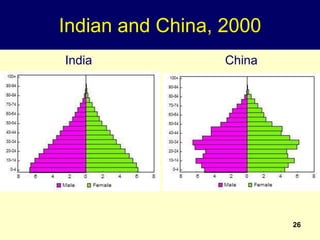
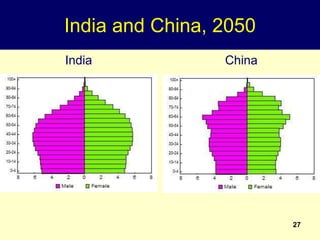
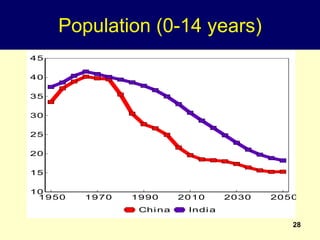
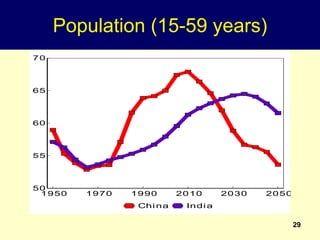
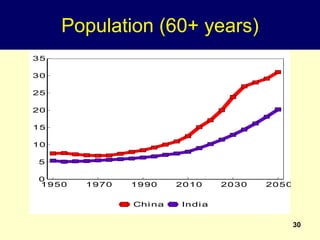
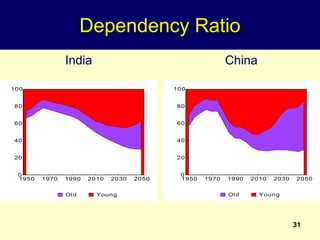
2. Rapid population growth can hinder development by increasing dependency ratios and diverting resources from investment. However, as fertility declines the "demographic dividend" of a rising share of working age people can spur economic growth if productively employed.
3. True integration of population and development requires addressing population factors like family planning within the broader context of social and economic development, rather than as an isolated intervention, to maximize welfare benefits.