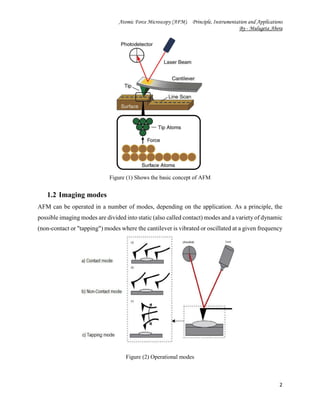
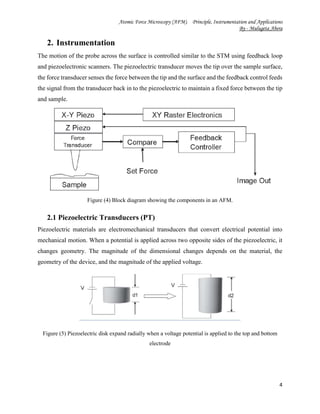
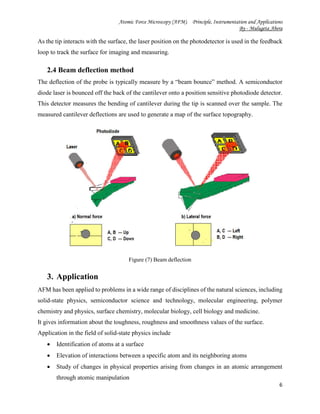
The document discusses the principles, instrumentation, and applications of atomic force microscopy (AFM). It was invented in the 1980s to overcome limitations of scanning tunneling microscopy. AFM uses a sharp tip to scan over a sample surface, detecting interatomic forces to generate topological images with atomic resolution without needing lenses or light. The key components are a cantilever with a tip, piezoelectric scanners, and a laser and photodetector that together detect tip deflection. AFM can operate in contact, non-contact, or tapping modes and is used in fields like materials science, biology, and nanotechnology due to its ability to image a wide range of surfaces.