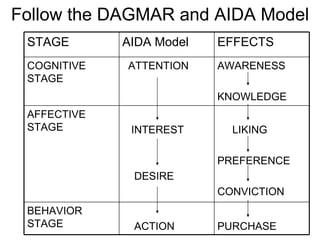
The document defines advertising and outlines steps for developing effective advertising programs. These include identifying the target audience, following the AIDA and DAGMAR models, and carrying out the five M's stages of mission, money, message, media, and measurement. The AIDA and DAGMAR models outline cognitive and affective stages to move consumers from awareness to action. The five M's provide a framework for setting objectives, deciding budgets, generating messages, selecting media channels, and evaluating effectiveness. The document also describes types of advertising such as informative, persuasive, and reminding ads.