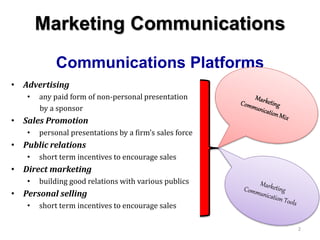
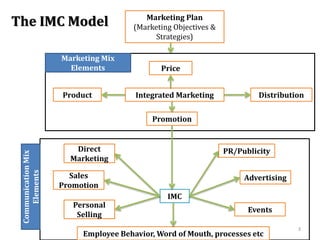
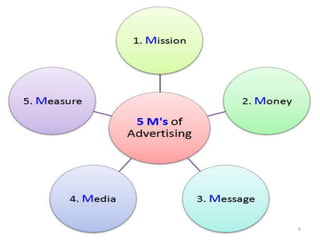
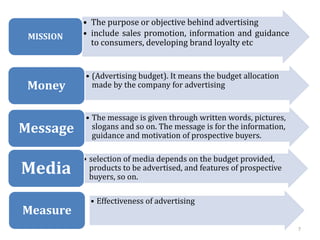
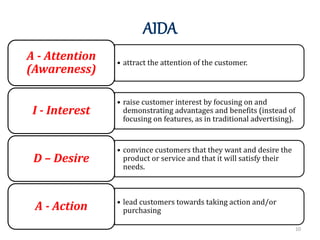
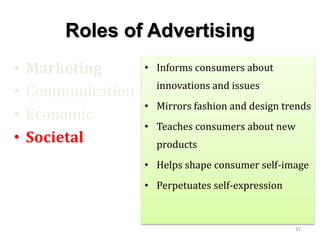
The document discusses marketing communications and integrated marketing communication (IMC). It defines various communication platforms including advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and direct marketing. It then introduces the IMC model and marketing mix elements. Several IMC examples are listed, followed by definitions and examples of various marketing communication models such as AIDA, DAGMAR, and others. The document concludes by covering ethical and social issues related to marketing communications.