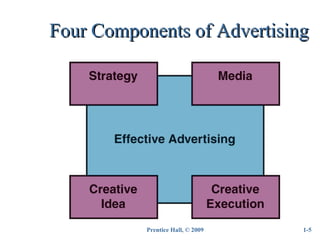
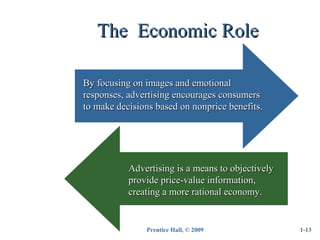
Advertising is defined as a complex form of communication used to impact consumer thoughts, feelings, and actions. It has evolved from simple images used for identification to mass communication used for promotion and sales. Modern advertising has five basic factors - it is paid communication that identifies a sponsor and tries to inform or persuade a large audience through various media. There are four components to advertising - strategy, creative idea, creative execution, and media planning/buying. It serves four roles - marketing, communication, economic, and societal. There are various types including brand, retail, direct response, and nonprofit advertising. The key players involved are the advertiser, agency, media, suppliers, and target audiences.