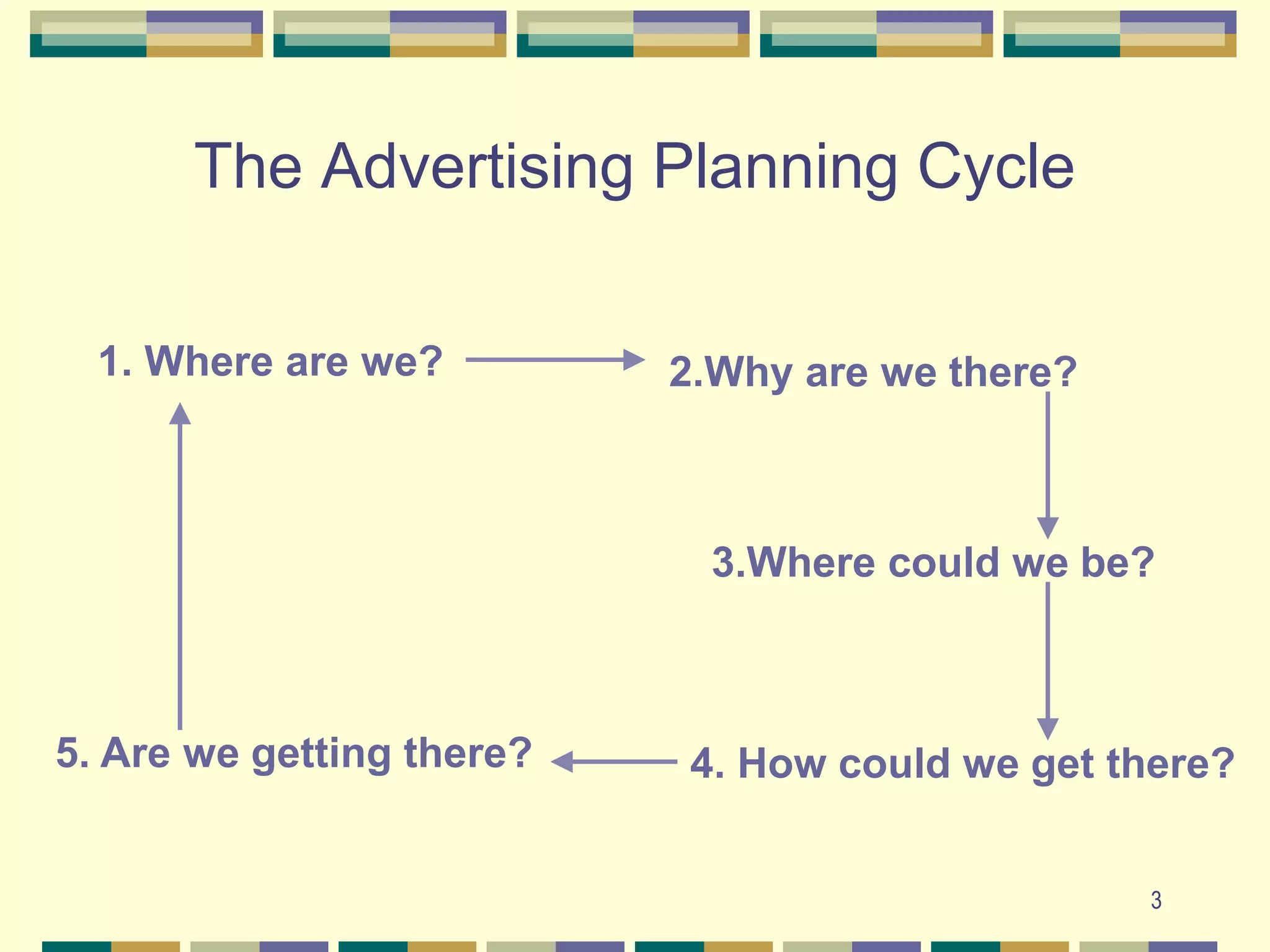
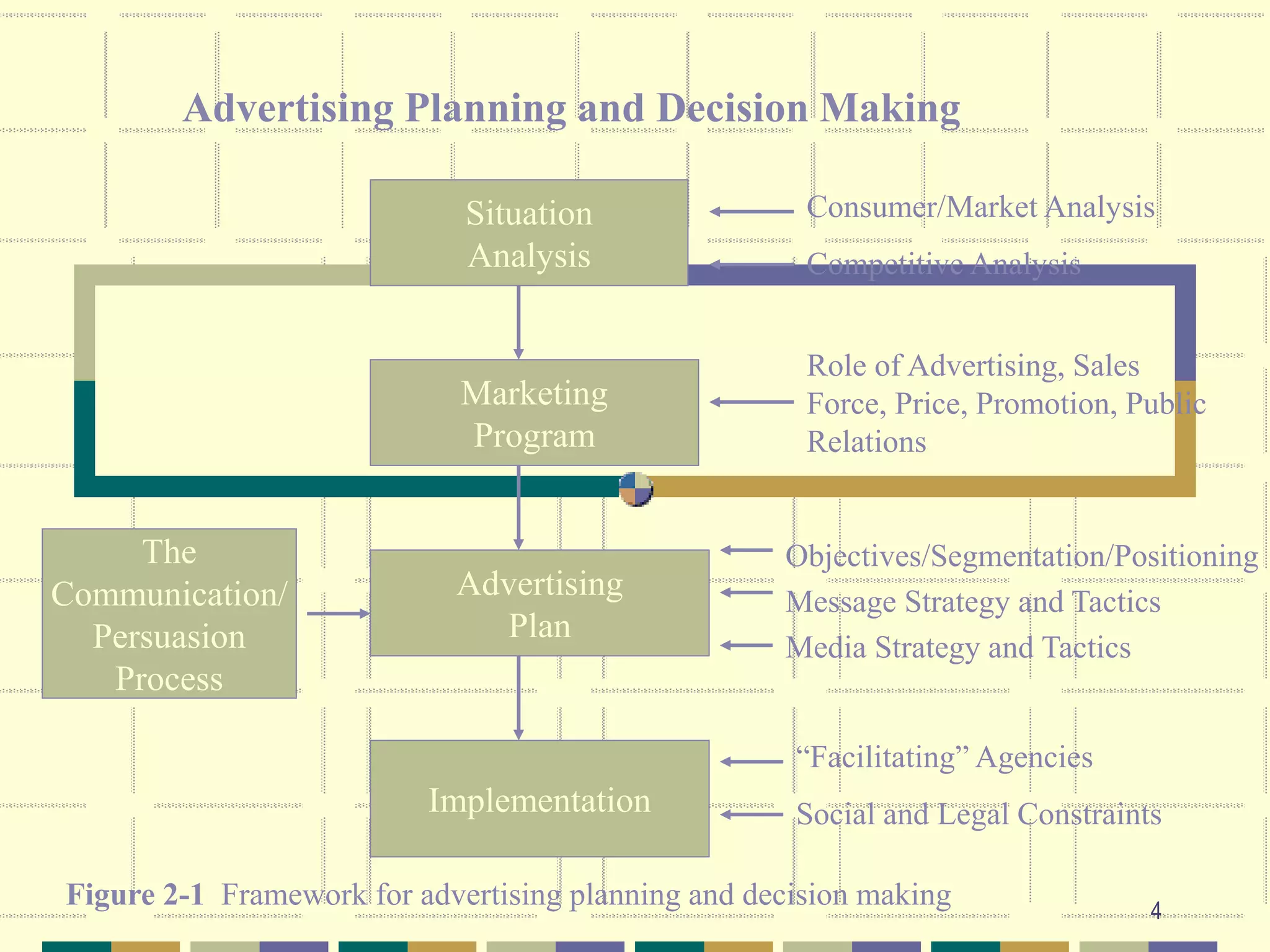
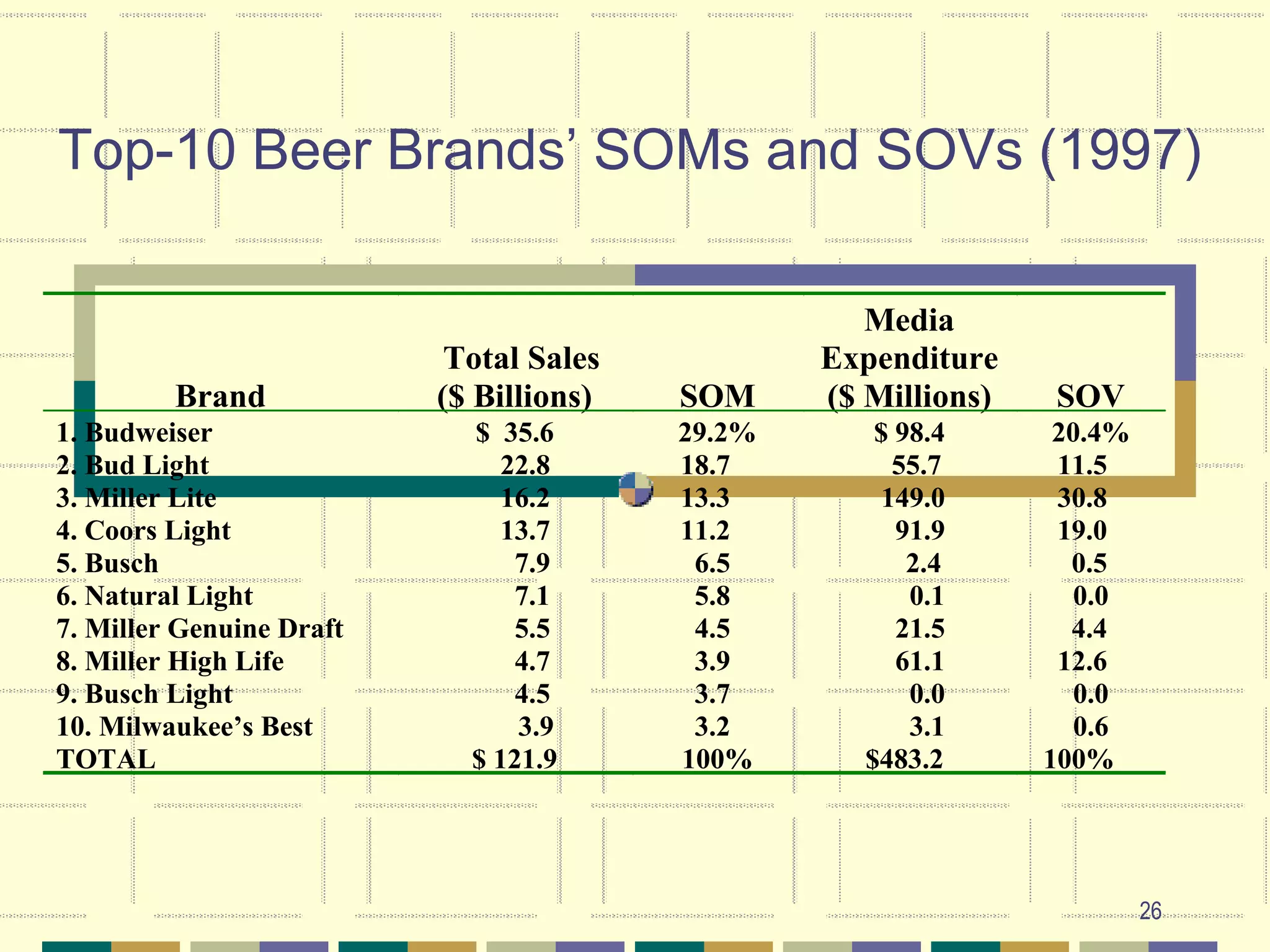
The document discusses key aspects of developing an advertising plan, including performing a situation analysis, setting objectives, developing message and media strategies, and determining budgets. It emphasizes the importance of setting measurable objectives that are specific to the target audience and timebound. Several methods for budgeting advertising are also reviewed, such as percentage-of-sales and competitive parity approaches. Factors related to new product advertising success and the relationship between advertising, sales, and profits are additionally examined.