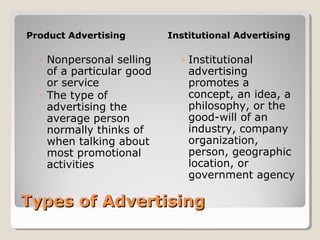
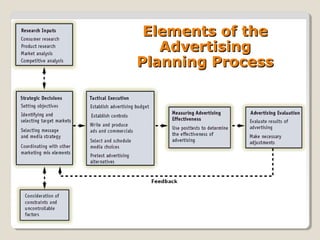
This document outlines the key aspects of the advertising planning process. It discusses the major types of advertising including product and institutional advertising. The major decisions in planning advertising are then explained as setting objectives like informing, persuading or reminding consumers, setting the budget, creating the advertising message, selecting media like television or magazines, and evaluating the advertising through pre-testing and post-testing. Objectives can aim to build primary or selective demand depending on the product life cycle stage. Factors like competition and media timing must also be considered in the planning process.