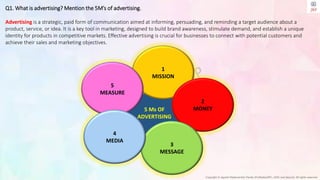
The document discusses advertising and its key components, including the 5M's: mission, money, message, media, and measure, which are crucial for effective advertising strategies. It also distinguishes between advertising and sales promotion, highlighting their different objectives and approaches, as well as outlining various types of advertising and sales promotion tools. Additionally, it covers the process of planning sales promotions, emphasizing the importance of setting objectives, selecting tools, and evaluating results.