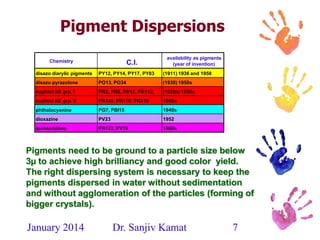
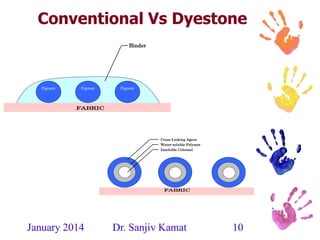
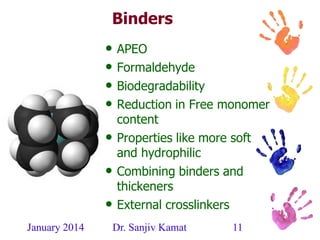
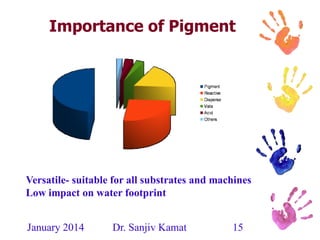
This document discusses the history and developments in pigment printing for textiles. It outlines that pigment dispersions have been used for over 3,000 years, initially using mineral pigments and natural polymers. Key developments included organic pigment dispersions in the 1920s, emulsion co-polymerization in the 1930s, and aqueous self cross-linking dispersions in the 1960s. More recently, improvements have focused on ecological factors like reducing emissions. The document also describes components of pigment printing systems and dispersions, as well as developments in binders, thickeners, and fixing agents to improve properties and reduce environmental impacts like formaldehyde and APEO content.