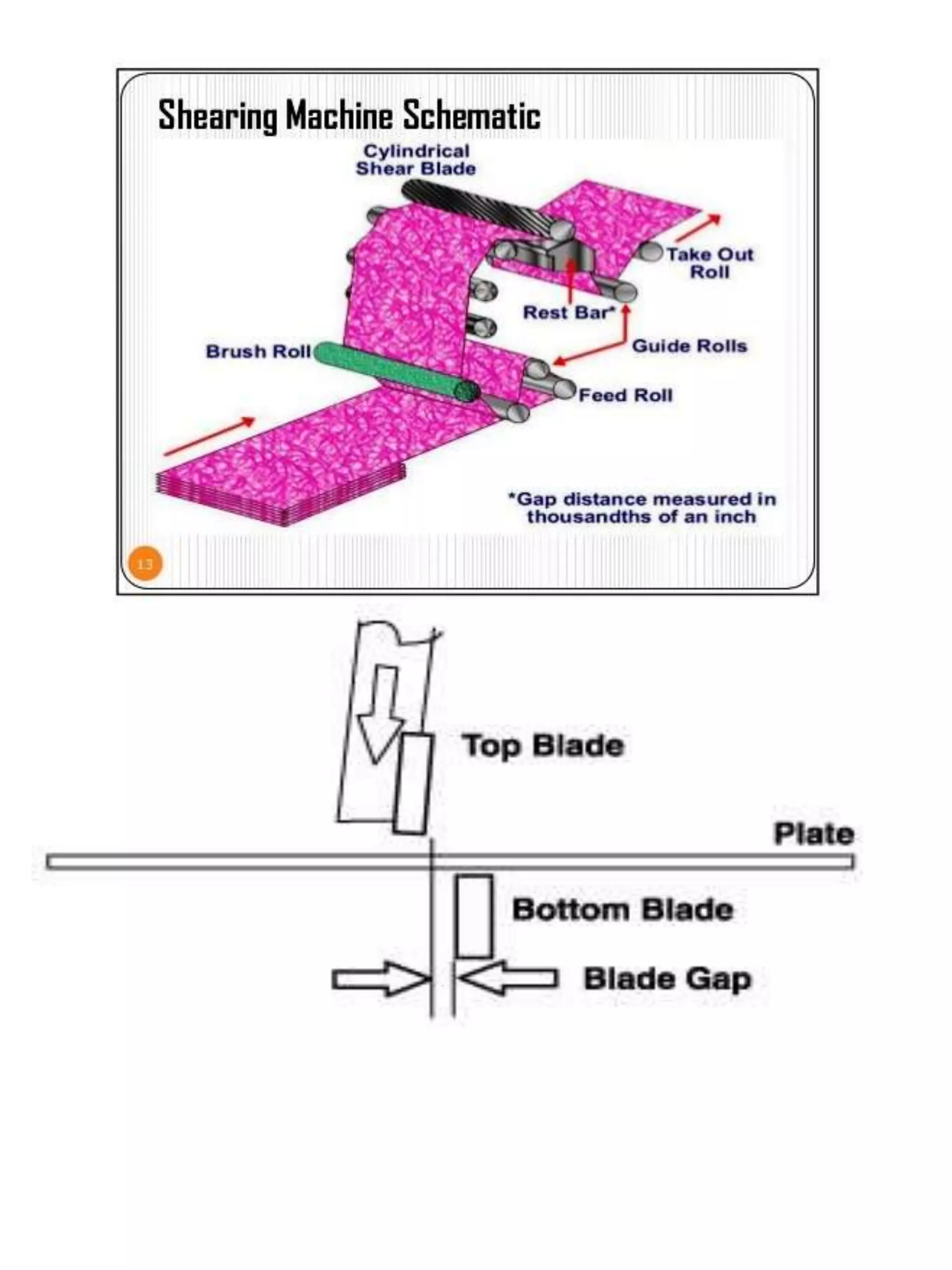
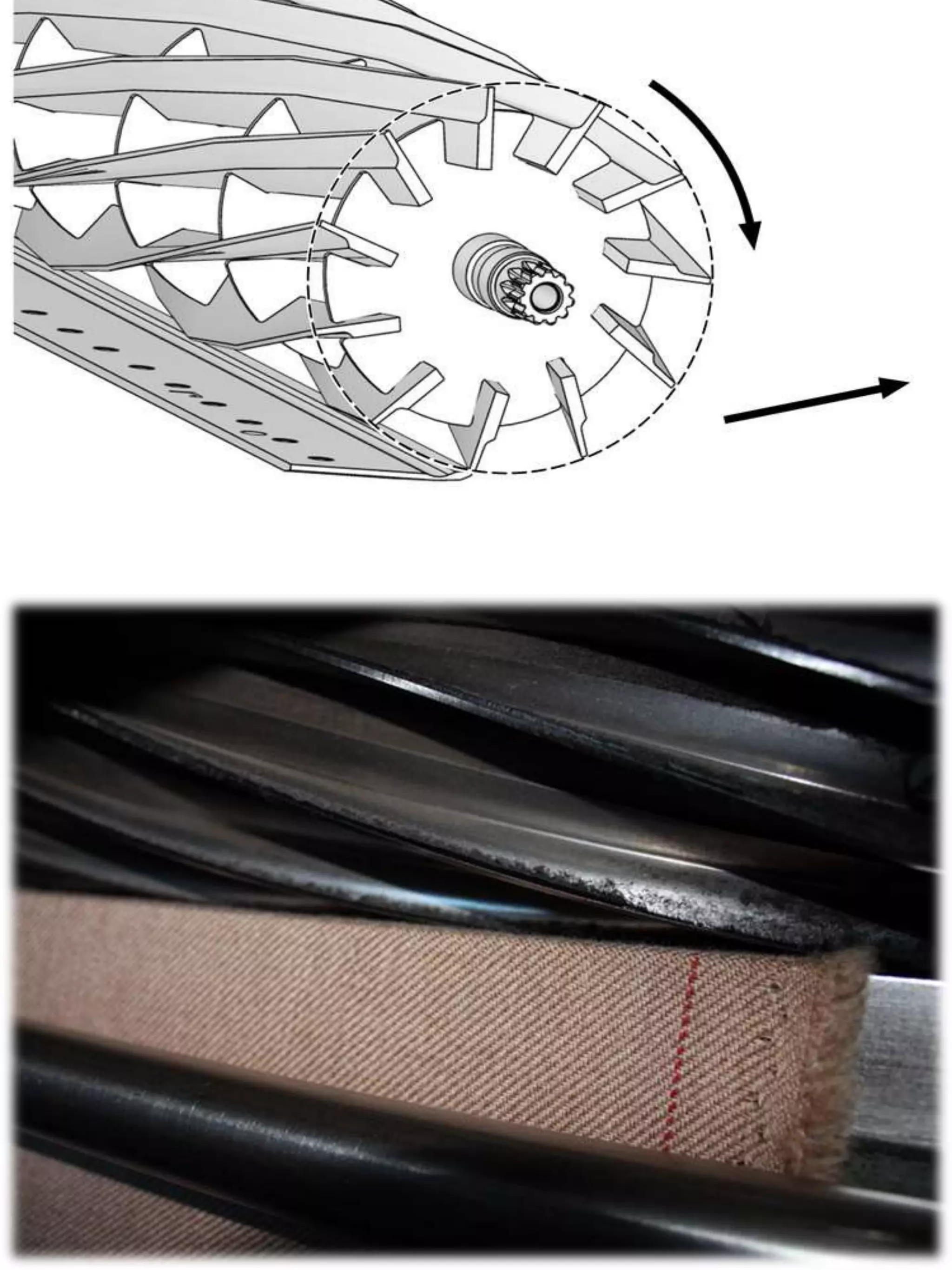
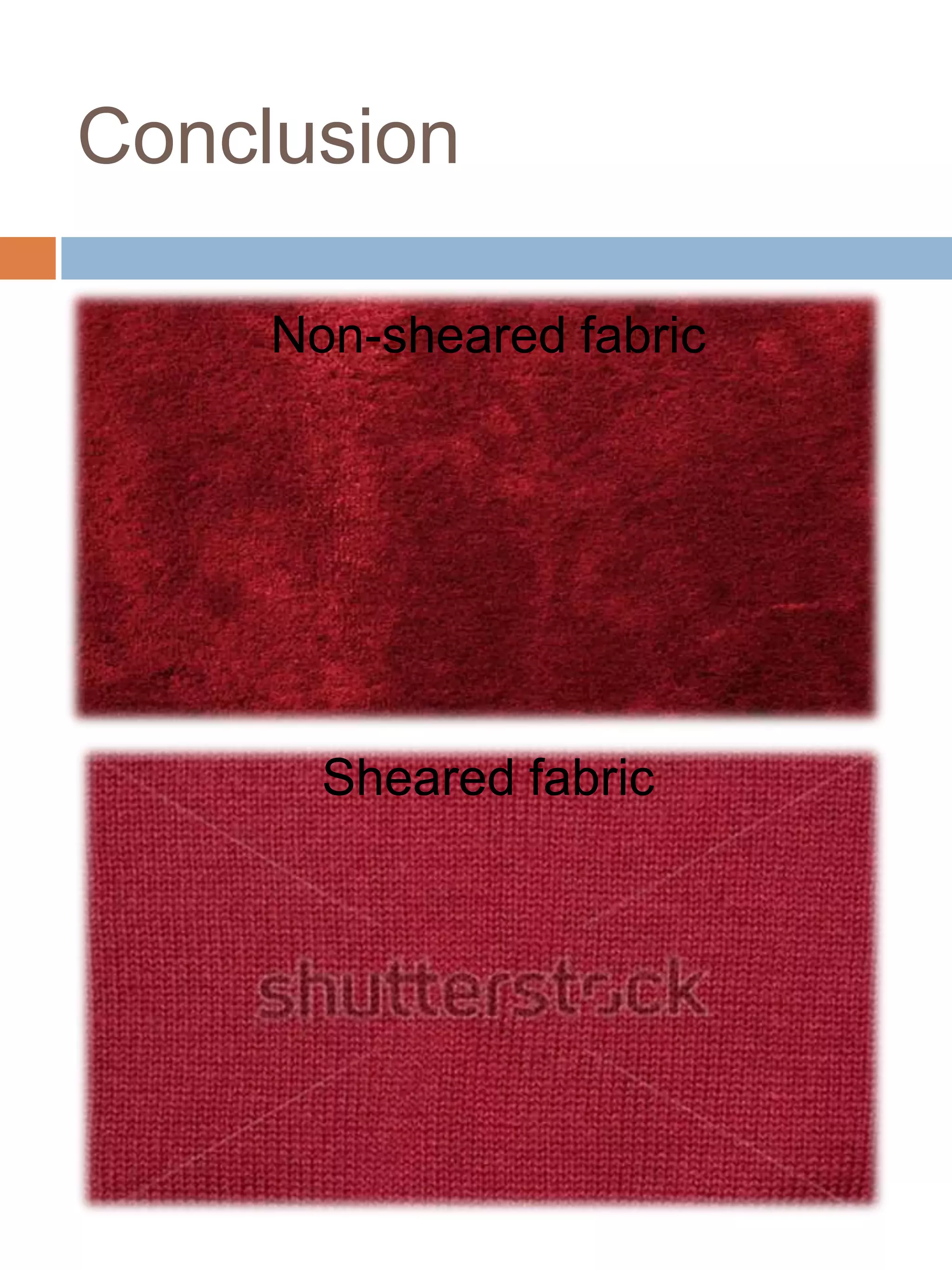
Cropping and shearing of wool fabric involves removing protruding fibers from the fabric surface using blades. Shearing has been used since the 15th century and was originally done manually. It is preferred over singeing for wool and other protein fibers because singeing can form convolutes on fiber tips, giving the fabric a harsh feel and uneven shade. The shearing process uses a series of helical blades that cut fibers as the fabric passes beneath, with an additional vertical blade to shear the other side. Objectives of cropping include removing surface fibers, giving a cleaner appearance and controlling pill formation. Advantages are increased flame retardancy, aesthetic properties, and ability to produce effects like hairiness. Downsides include being slower and requiring