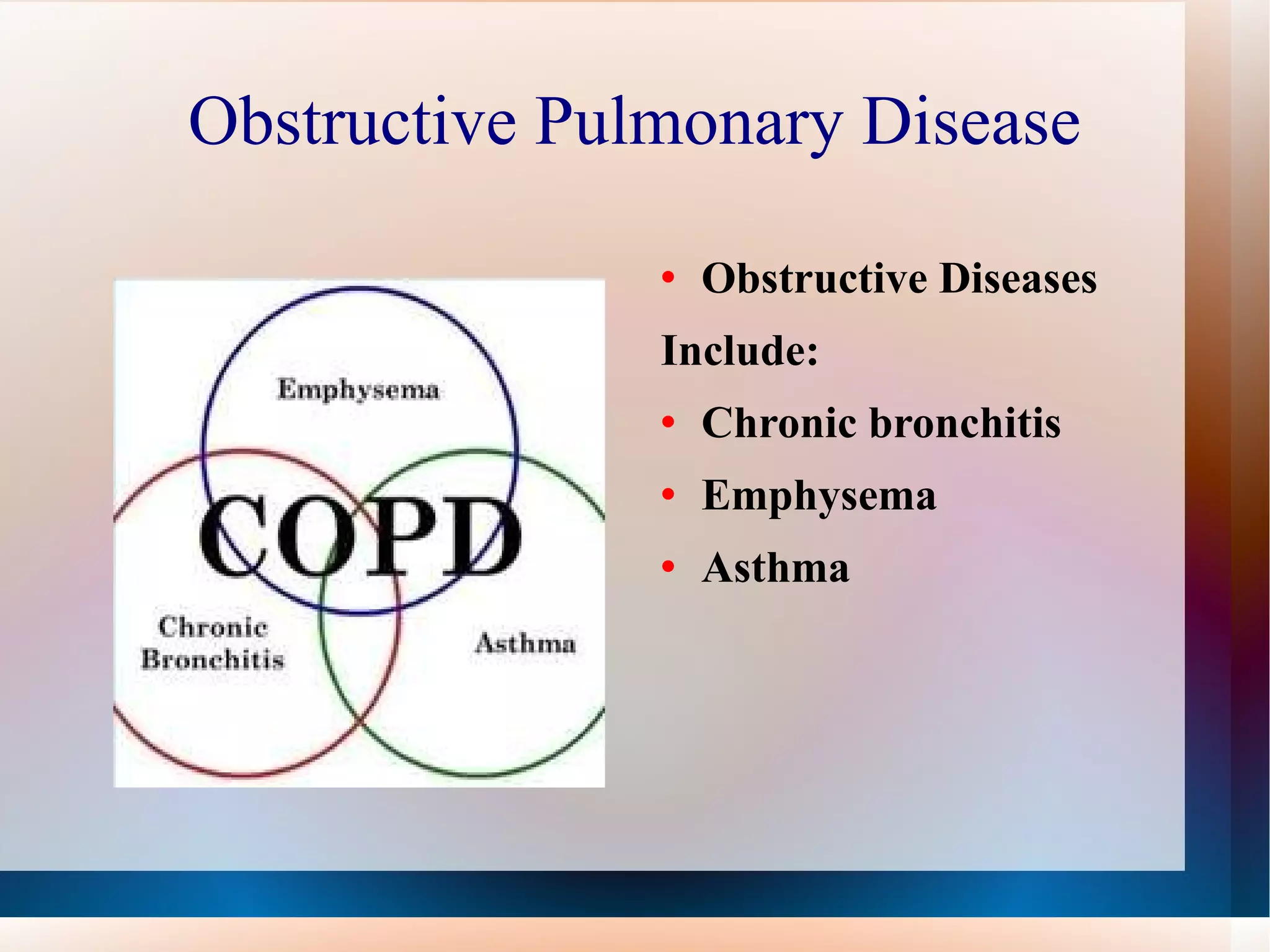
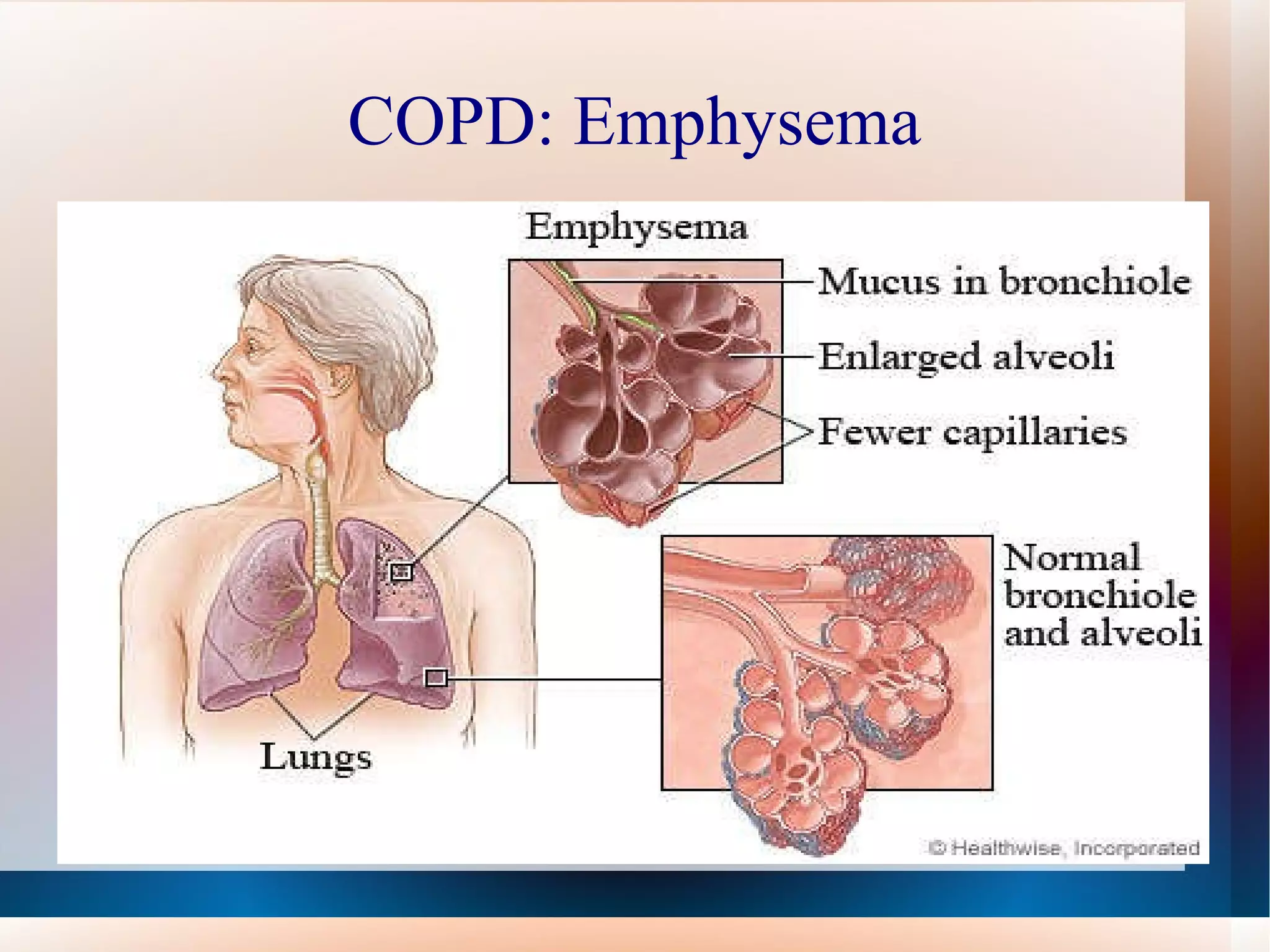
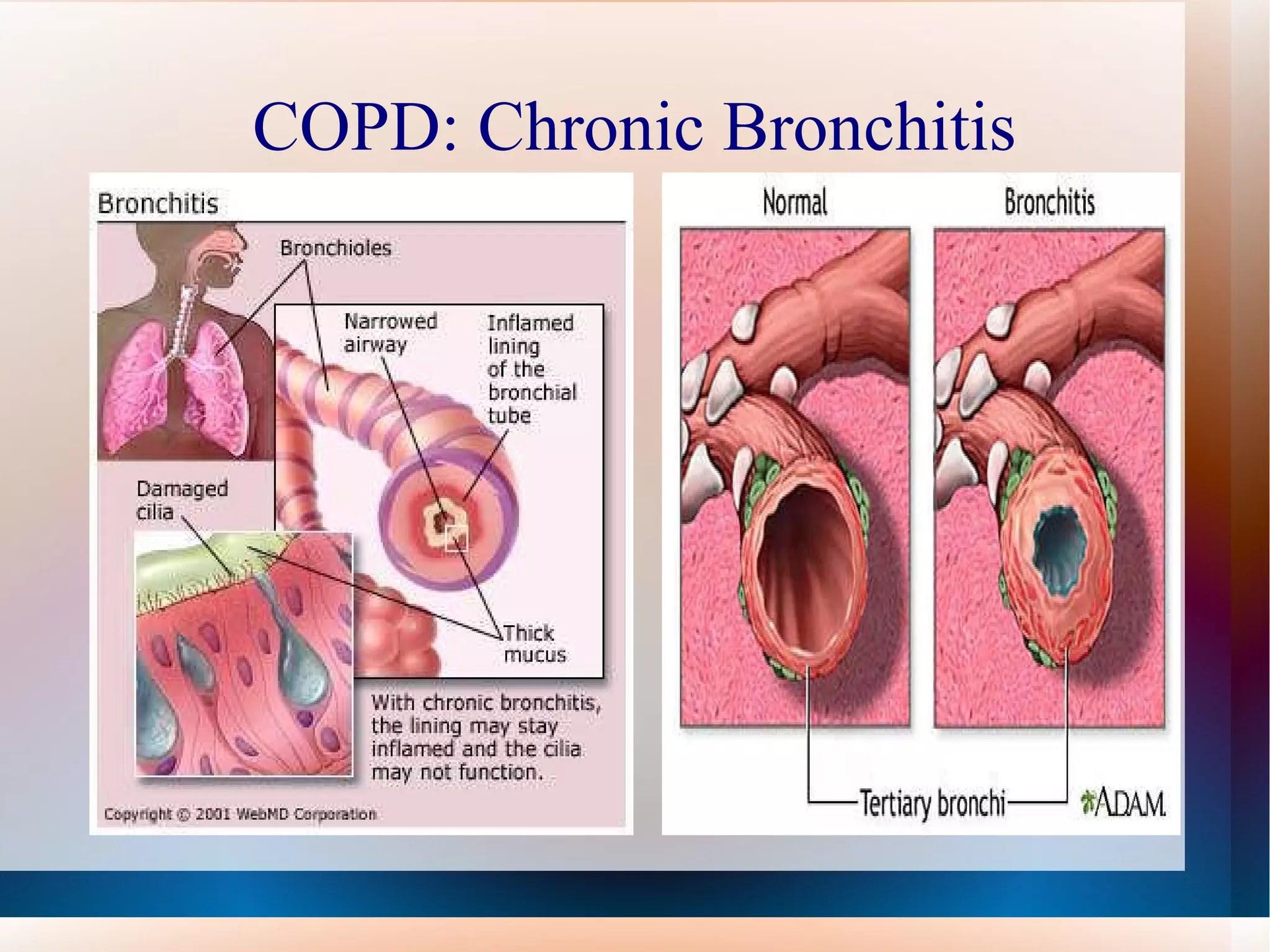
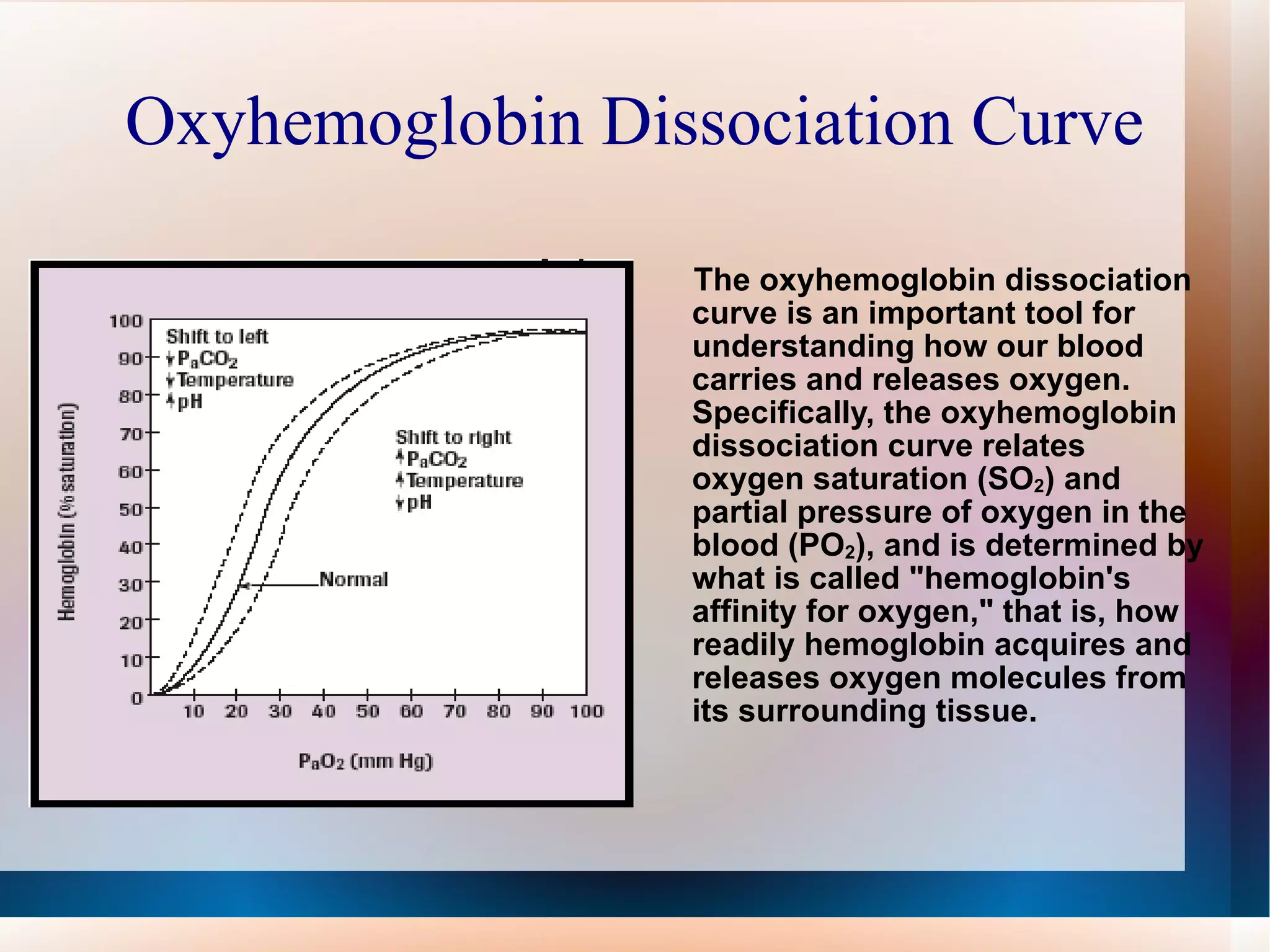
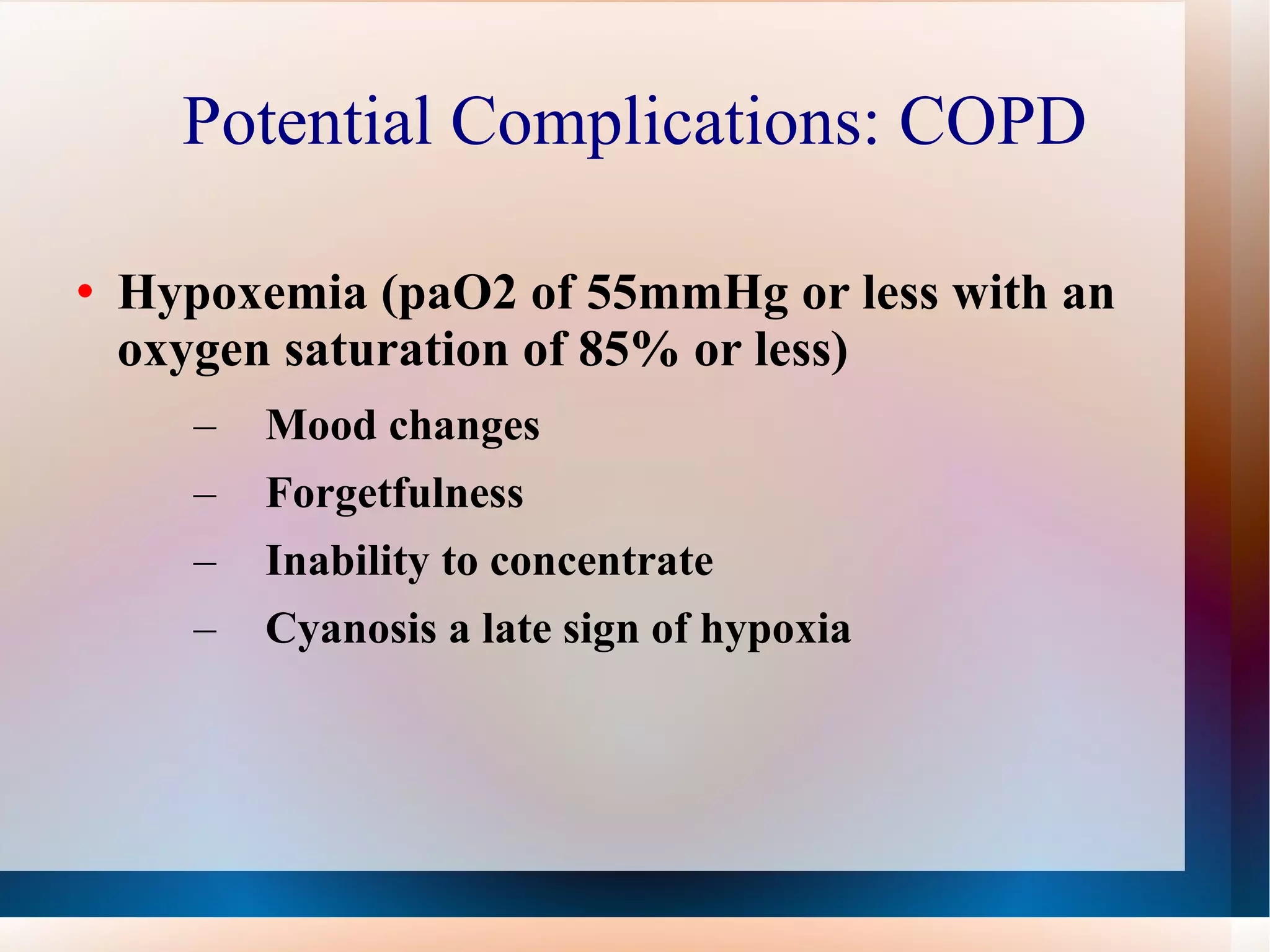
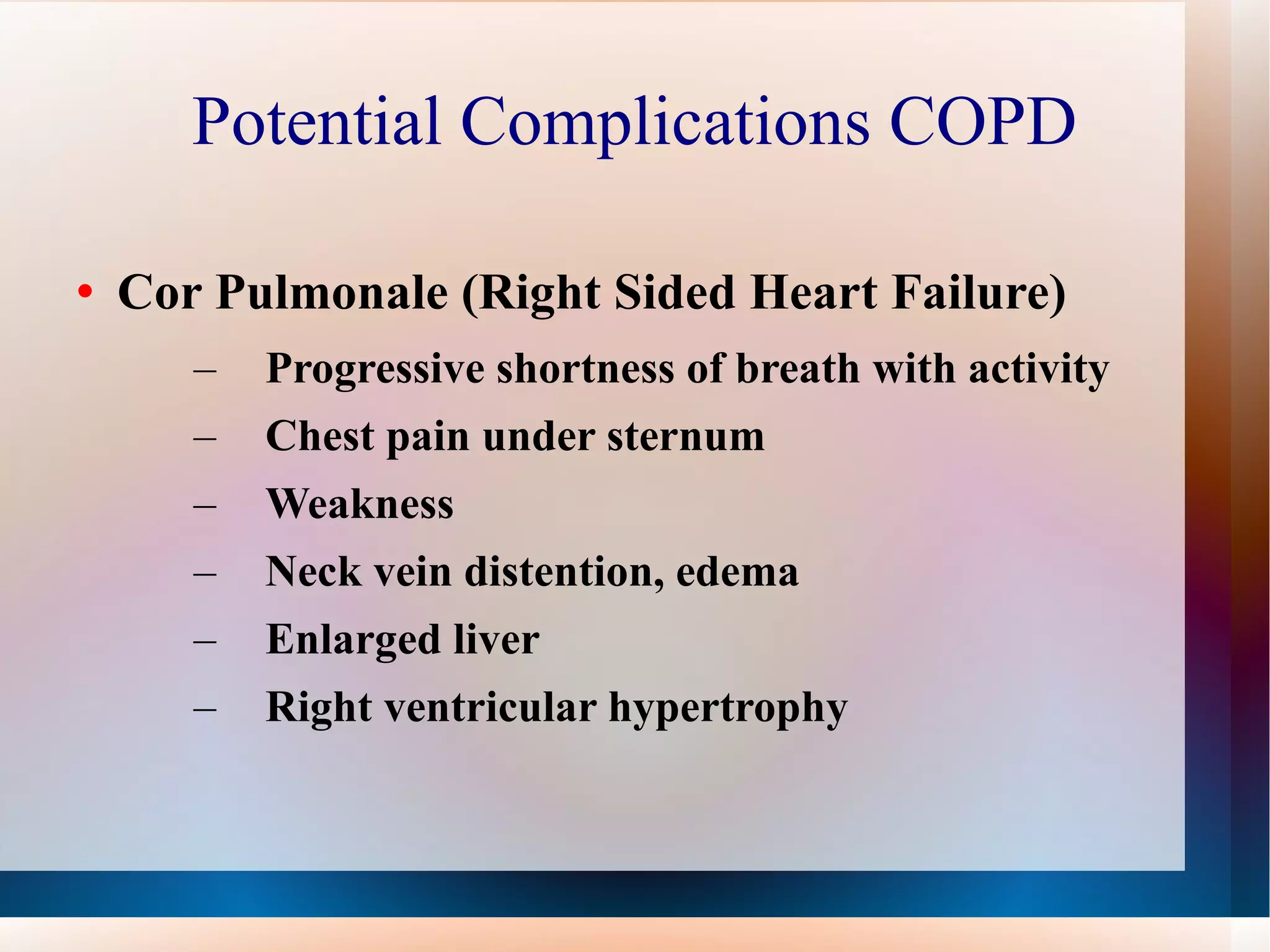
Obstructive lung diseases are a group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing problems, including chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and sometimes asthma. Key characteristics include inflammation and damage to airways and lung tissue that impair gas exchange and cause symptoms like shortness of breath. Smoking is the primary risk factor. Symptoms are evaluated through medical history, exams, and pulmonary function tests. Treatment focuses on reducing symptoms, improving lung function, and managing exacerbations through medications, breathing exercises, smoking cessation, flu vaccines, and oxygen therapy if needed. Nurses play an important role in patient education, monitoring for complications, and helping patients properly manage their condition.