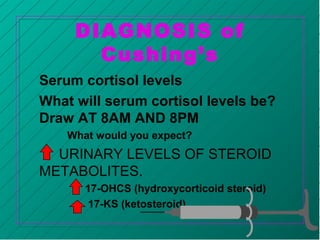
The adrenal glands produce important hormones that regulate salt, sugar, and sex functions in the body. The adrenal cortex produces mineralocorticoids like aldosterone which regulate sodium and potassium levels, and glucocorticoids like cortisol which regulate carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. The adrenal medulla produces catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine which trigger the fight or flight response. Diseases can result from too much or too little production of these hormones. Cushing's disease occurs when there is too much cortisol and causes weight gain, high blood pressure, and easy bruising. Conn's syndrome features too much aldosterone and causes high blood pressure and low potassium