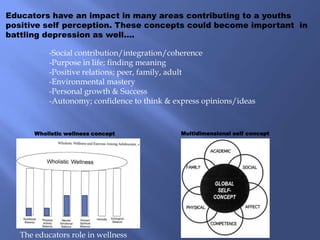
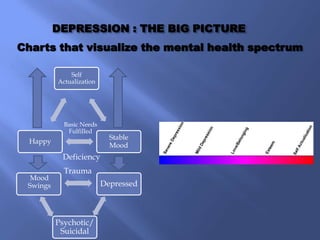
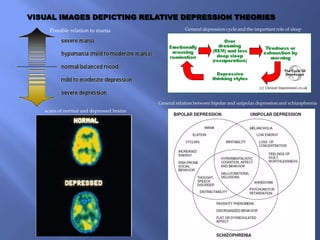
The document discusses the complexities of depression during adolescence, highlighting its onset, triggers, and the interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. It emphasizes the importance of understanding root causes for effective treatment, prevention strategies in educational settings, and the role of educators in promoting mental wellness. Furthermore, it addresses the concerns associated with antidepressant medications and the potential benefits of natural health approaches and alternative therapies.