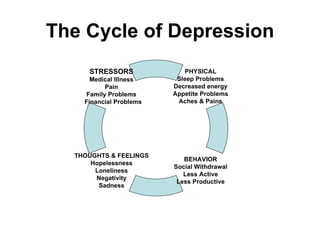
This document provides information about identifying and understanding depression. It begins with course objectives about learning the signs and symptoms of depression and how it differs from typical sadness. It then discusses statistics about depression prevalence and treatment rates. The rest of the document defines depression, discusses types and causes, risk factors, diagnosis process, and impact on emotions, physical health, and behavior. It also covers treatment options like medication and self-help strategies. The goal is to educate about depression and help those suffering from it to seek appropriate help and treatment.