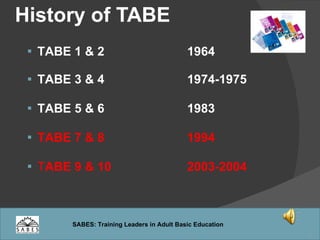
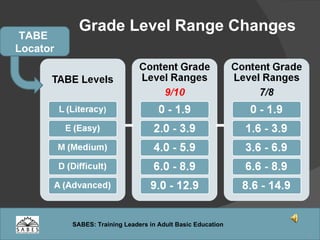
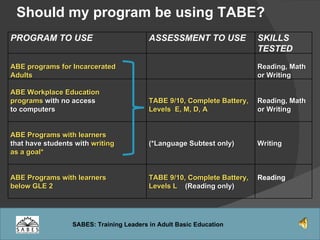
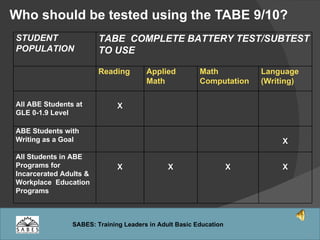
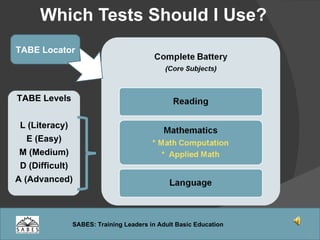
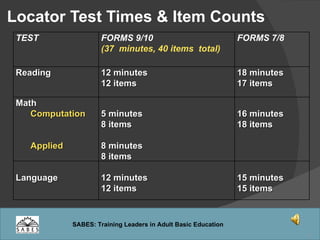
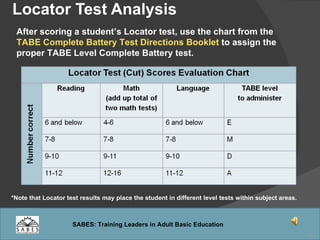
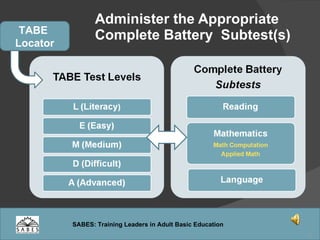
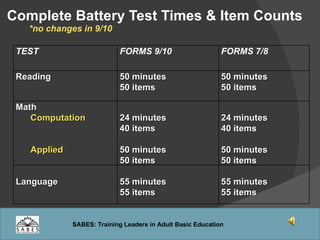
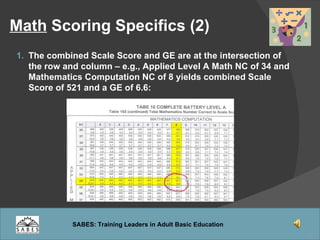
This document provides an overview of administering and scoring the TABE 9/10 standardized test. It discusses the history and purpose of TABE testing in Massachusetts, differences between TABE forms 7/8 and 9/10, appropriate use of the TABE locator test and levels, administration procedures, scoring, and requirements for competency in TABE administration.