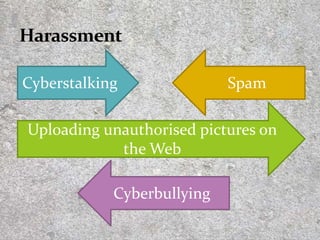
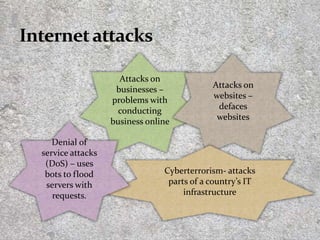
This document discusses techniques and tools of cybercrime. It defines various types of malware like viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. It also explains social engineering techniques used by cybercriminals like phishing and pretexting to trick users into revealing private information. The document also covers categories of computer crimes and provides tips on protecting yourself from computer crimes like using antivirus software, having strong passwords, and avoiding opening suspicious attachments or clicking links from unknown sources.