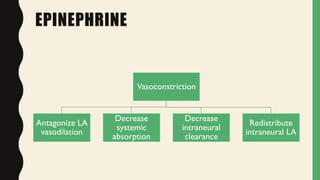
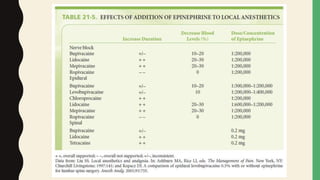
This document discusses common adjuncts and additives used with local anesthetics for nerve blocks and spinal anesthesia. It describes how epinephrine prolongs the duration and intensity of nerve blocks by causing vasoconstriction. Alkalinization can increase the effectiveness of local anesthetics but risks of precipitation limit its usefulness. Opioids and alpha-2 adrenergic agonists provide analgesic effects when added to local anesthetics by binding to receptors in the spinal cord. Fentanyl and morphine are commonly used opioid adjuncts. Dexamethasone may also prolong the duration of local anesthetic nerve blocks when used, though the mechanism is unknown.