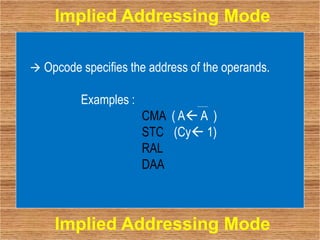
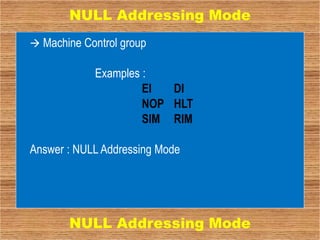
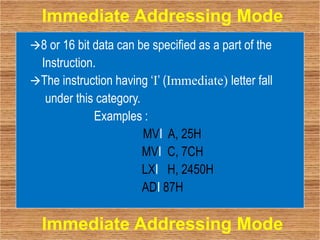
This document discusses the different addressing modes of the Intel 8085 microprocessor. It describes 5 addressing modes: immediate, register, direct, indirect, and implied. Immediate mode embeds data in the instruction. Register mode transfers data between registers. Direct mode specifies the operand address in the instruction. Indirect mode uses a register pair to hold the operand address. Implied mode uses just the opcode to specify the operands.




![The memory address where the operand located is
specified by the contents of a register pair.
Examples :
LDAX B
MOV A, M (M: H-L pair in 8085)
Immediate Indirect MVI M,55H
Register Indirect ADC M [A A +Cy+(M)]
DCR M [(HL)(HL)+1]
PUSH PSW
Indirect Addressing Mode
Indirect Addressing Mode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8085addressingmodeshabibur-200827150015/85/Addressing-Modes-of-8085-Microprocessor-6-320.jpg)