The Polish lower-secondary school maths curriculum covers the following topics over three years (classes):
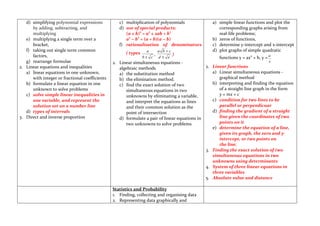
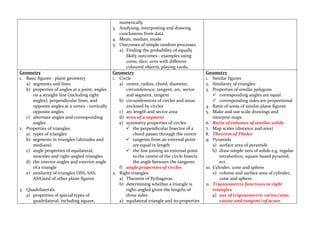
1) Arithmetic - operations on rational numbers, percentages, indices, roots, and real numbers.
2) Algebra - algebraic expressions, linear and quadratic equations, functions, and simultaneous equations.
3) Geometry - properties of angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, similarity, trigonometry, and 3D shapes.
4) Statistics and probability - collecting and representing data, measures of central tendency, and probability.
Additional non-curricular topics are also sometimes introduced to prepare students for math contests, including complex numbers, vectors, and calculus concepts.