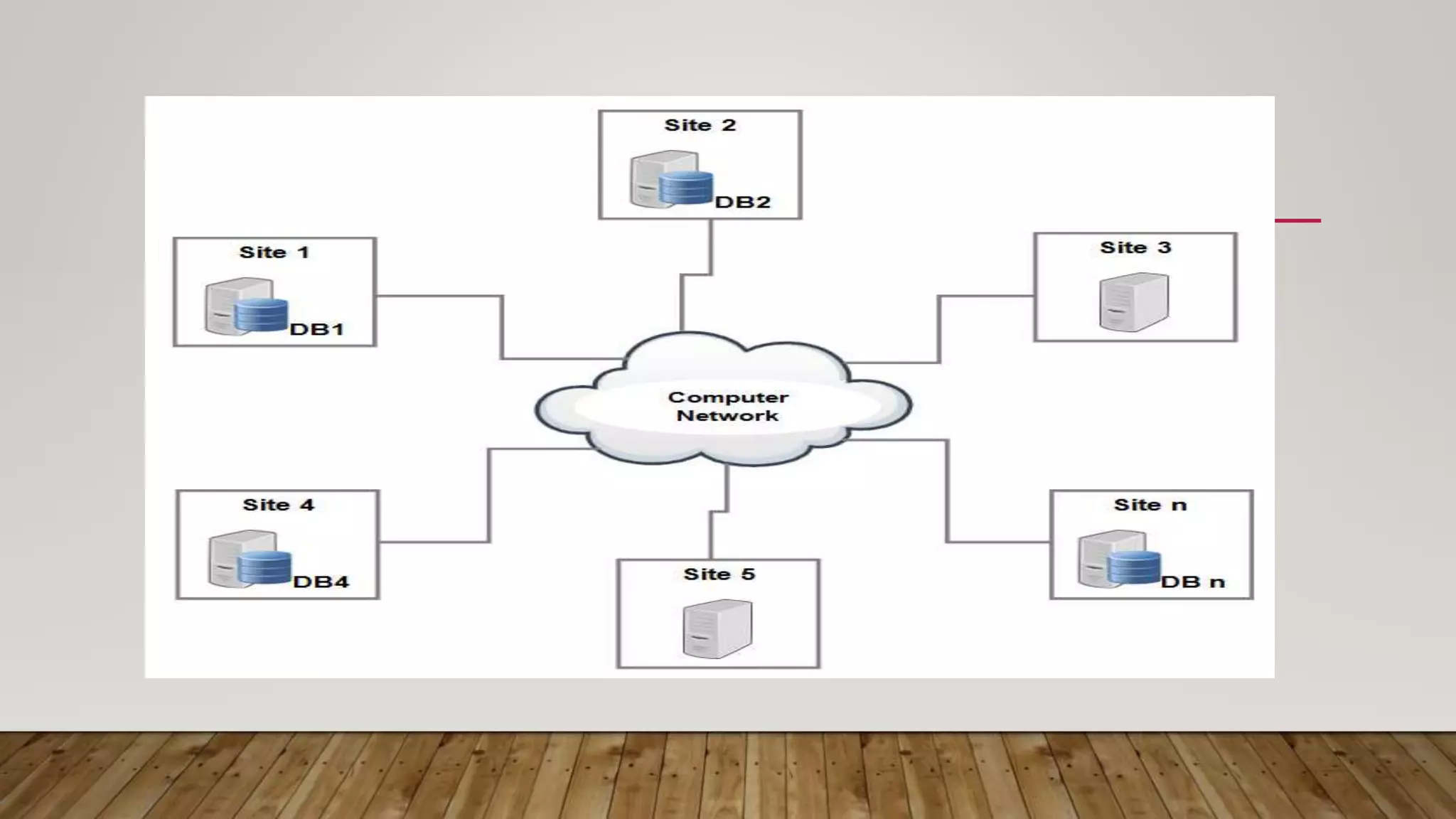
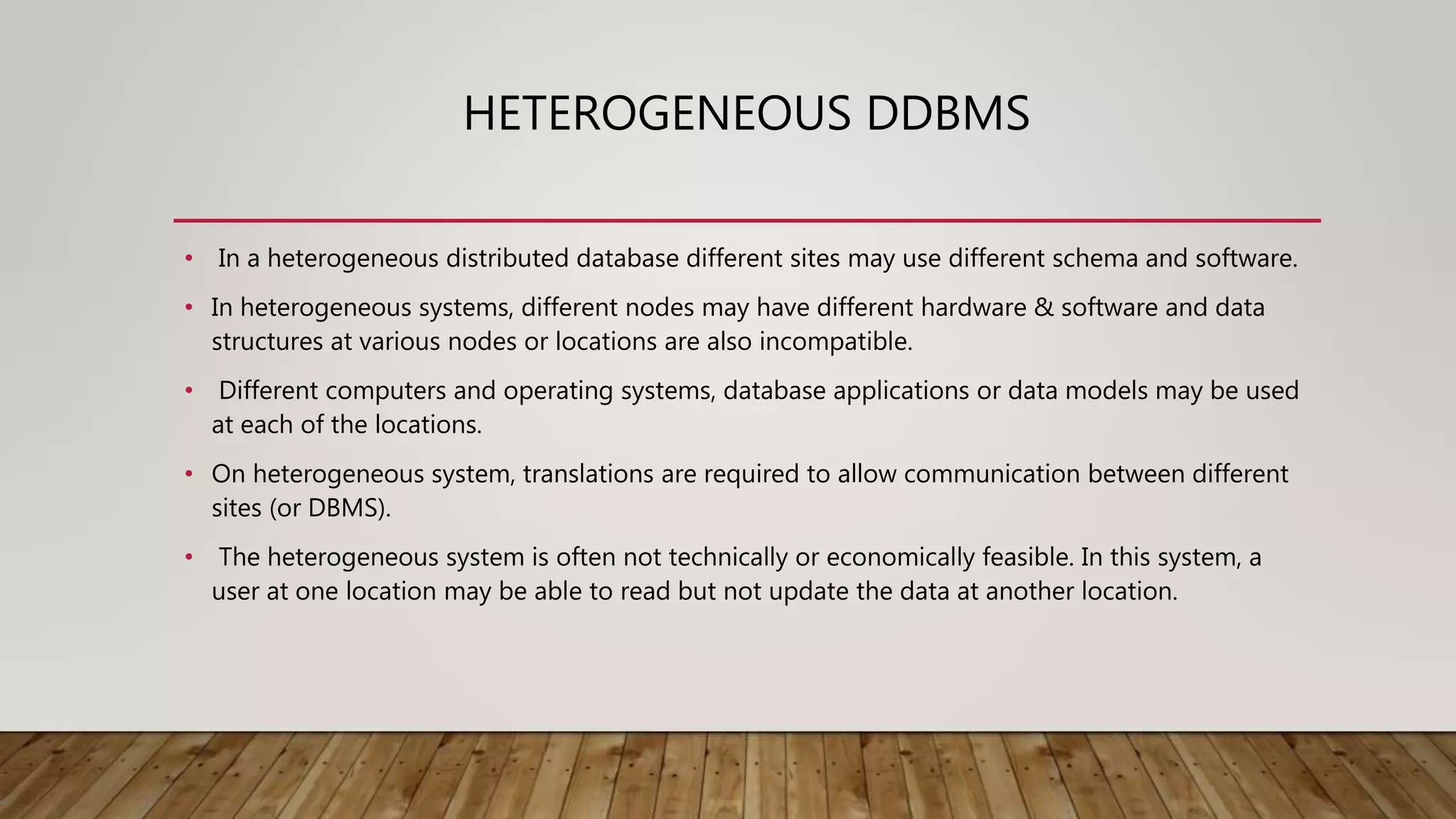
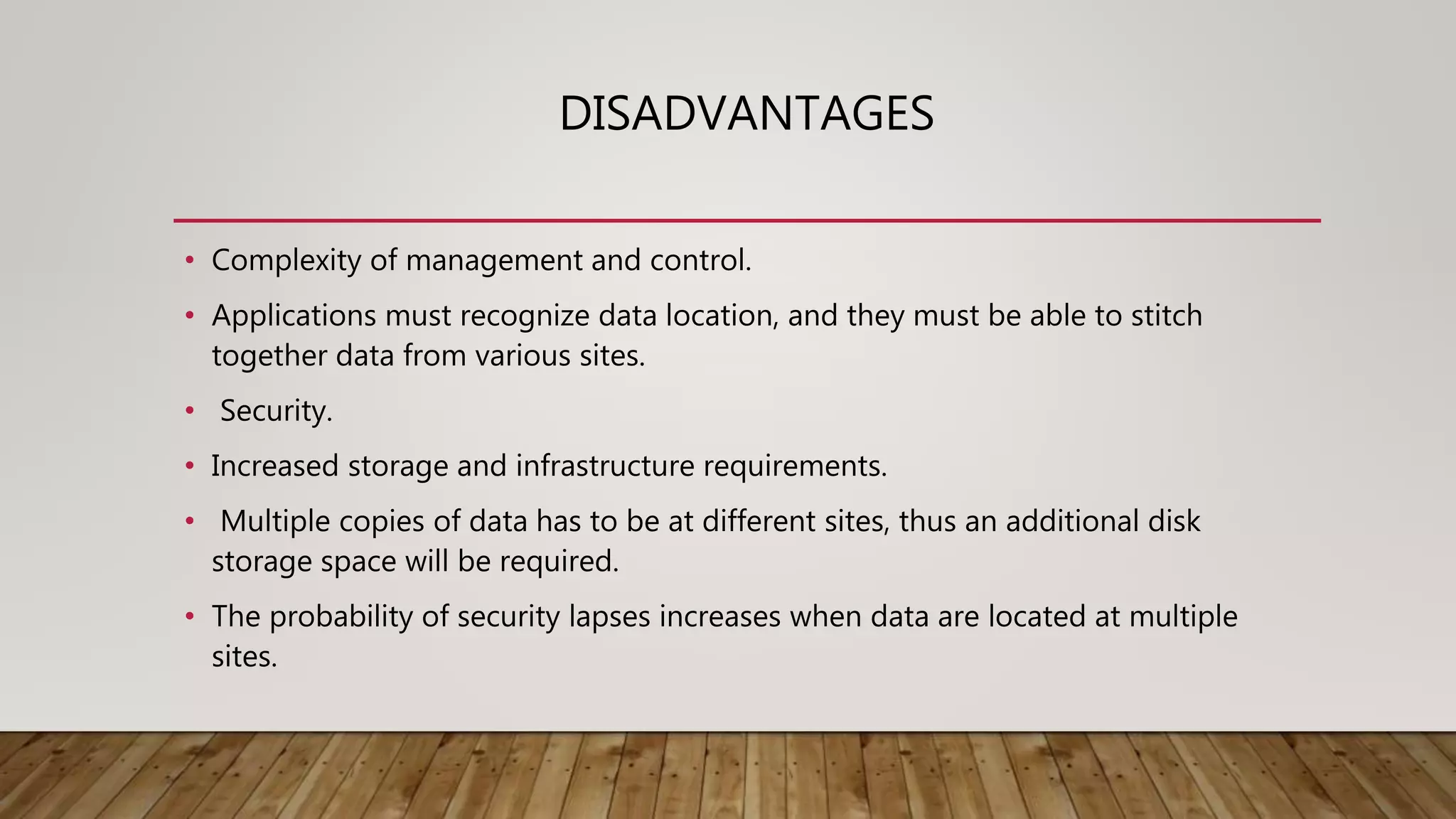
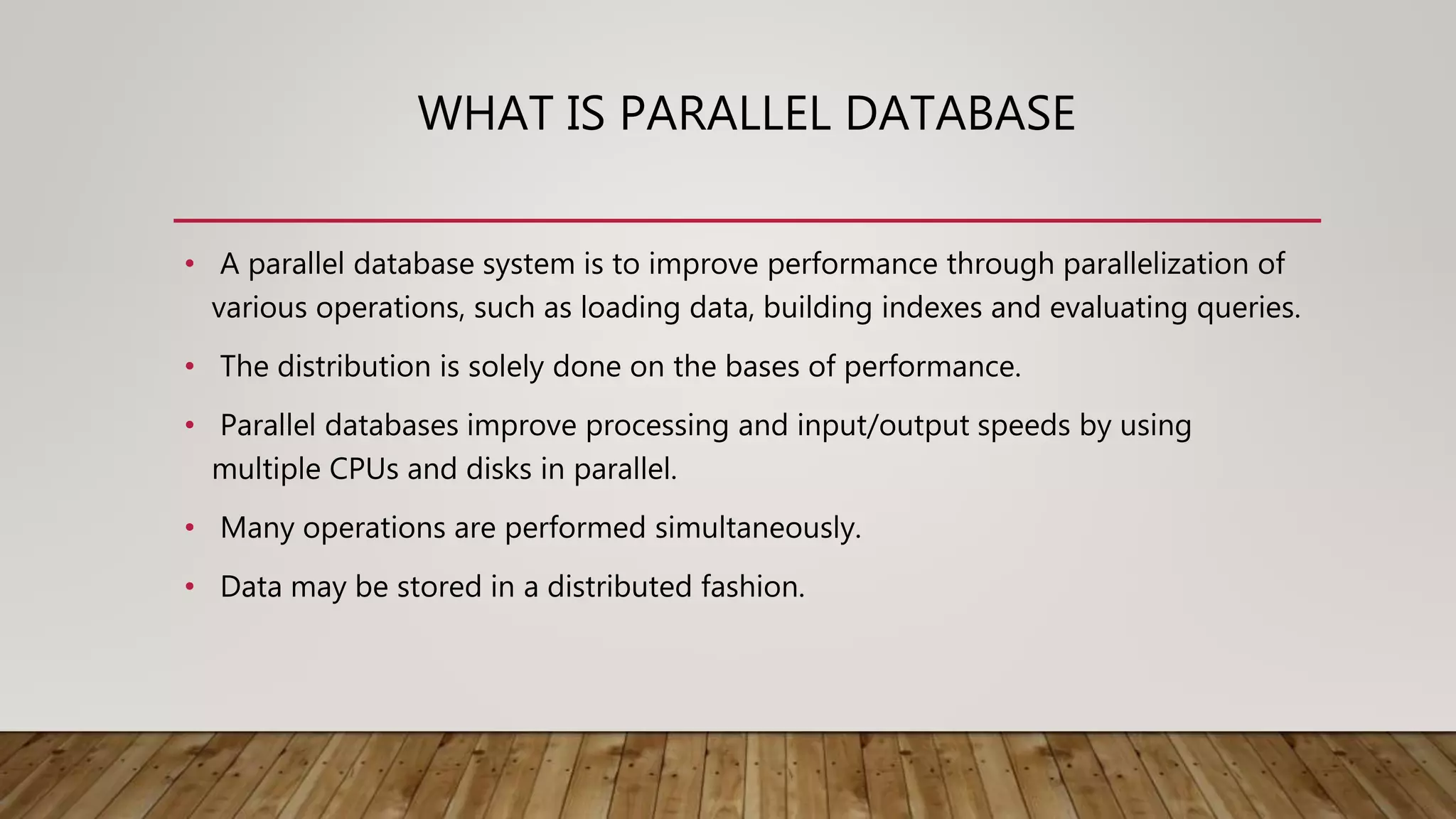
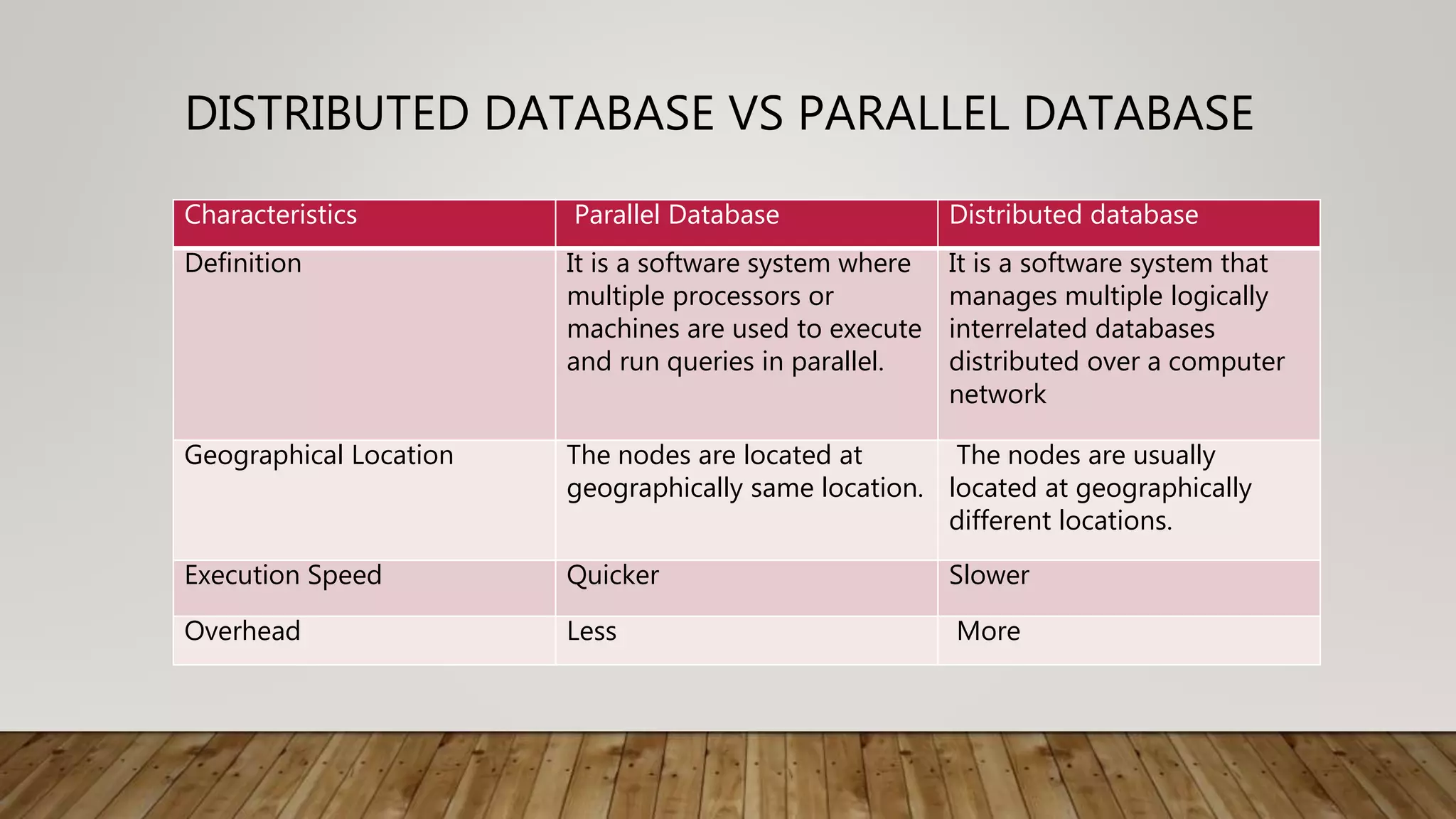
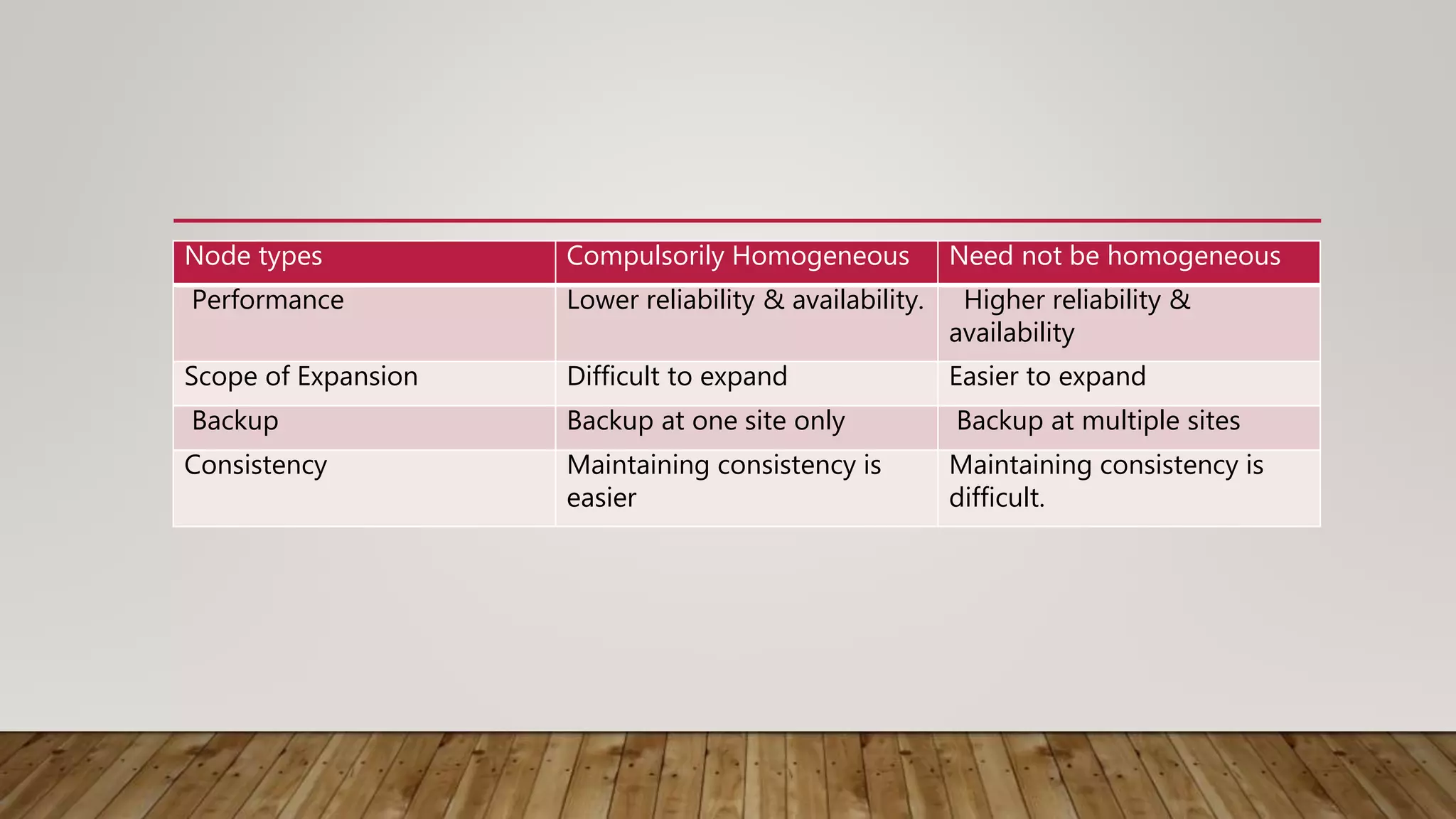
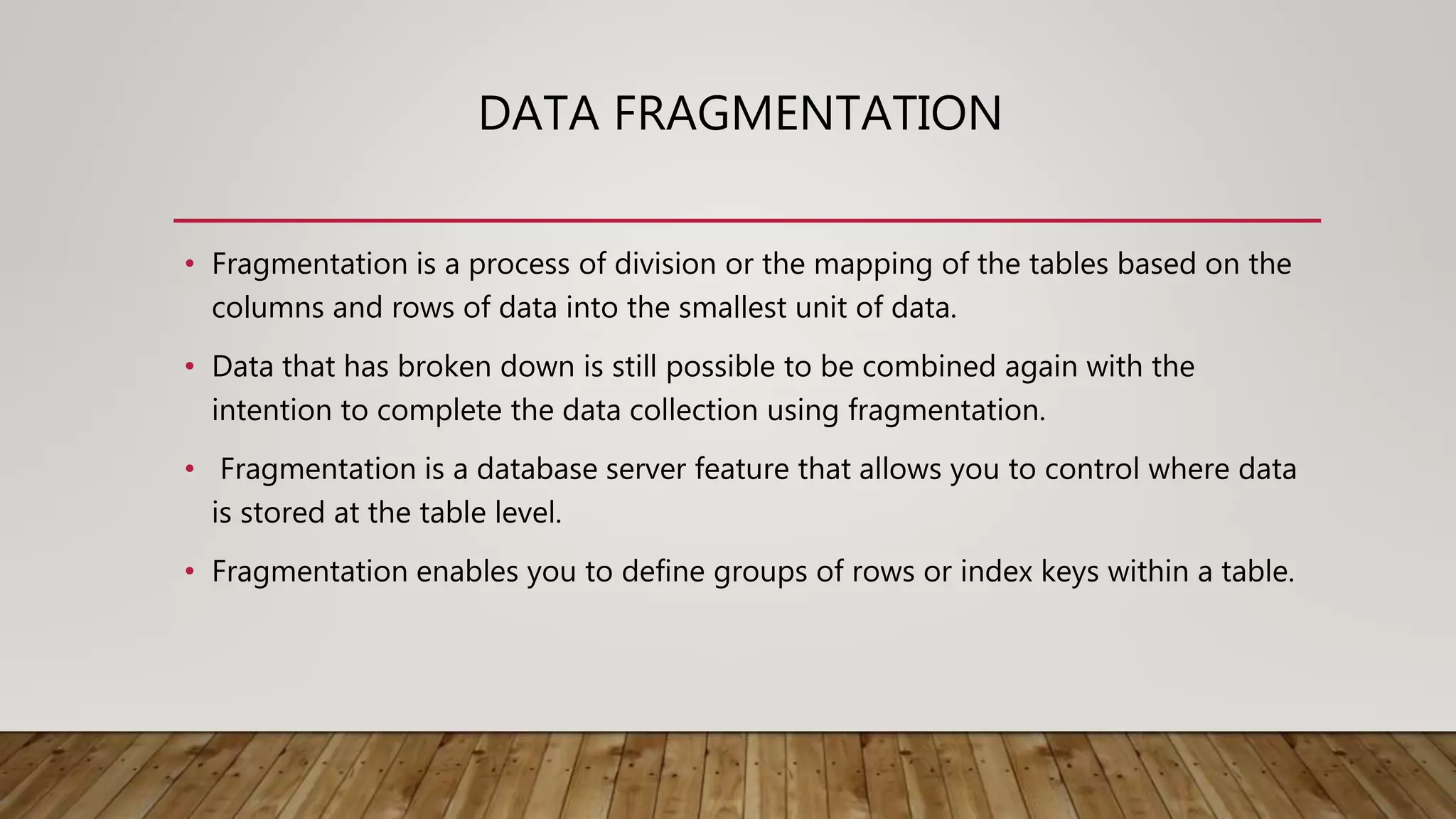
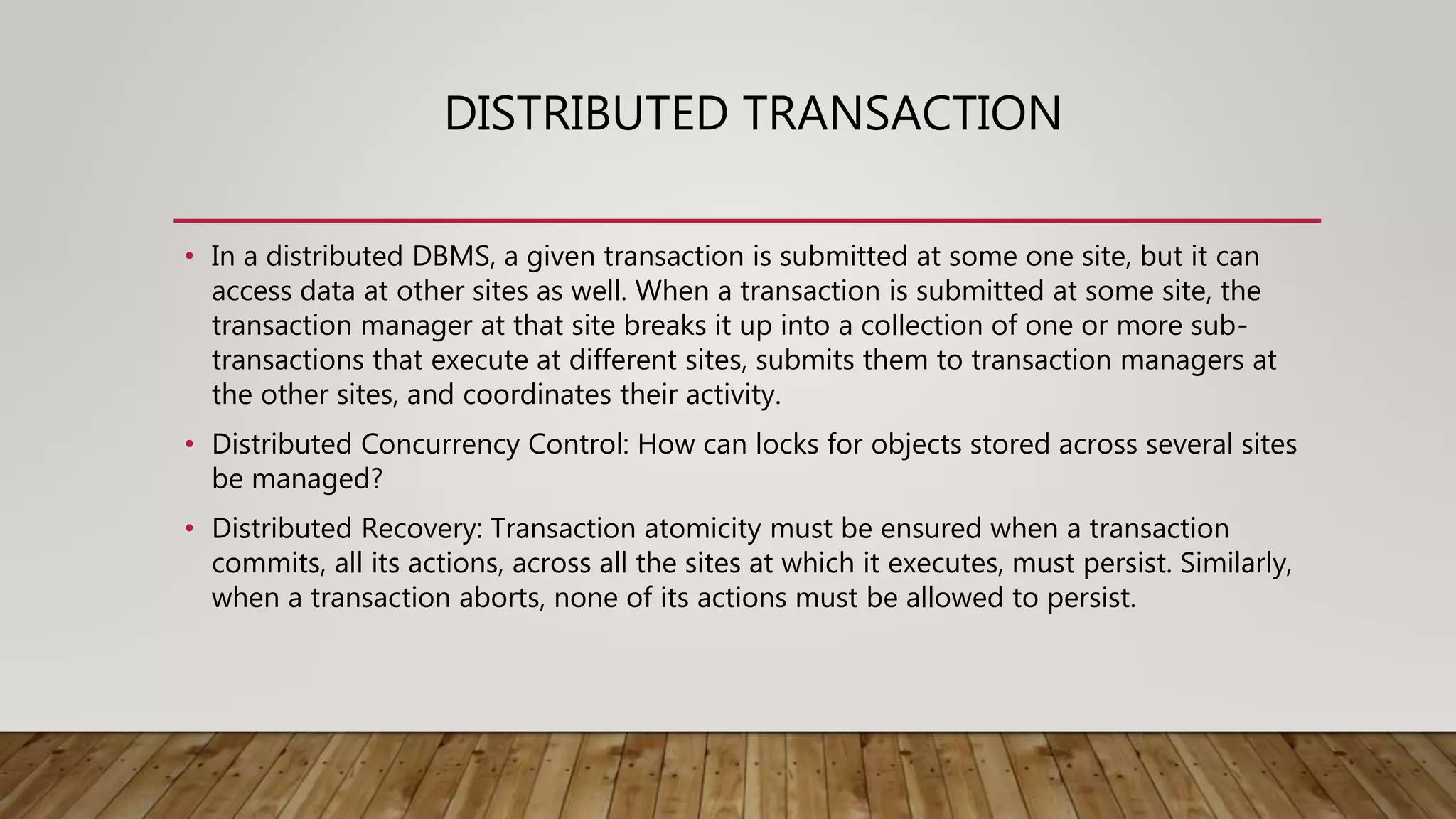
A distributed database (DDB) is a collection of logically related databases distributed across a computer network. It allows data and processing to occur at multiple sites. Key characteristics include data fragmentation across sites, replication of fragments for availability and performance, and distributed transaction management to ensure consistency. The main types are homogeneous DDBMS, where all sites use identical software, and heterogeneous DDBMS where different sites may use different systems. Challenges include complex management, security, and maintaining consistency across sites.