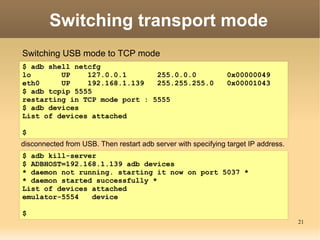
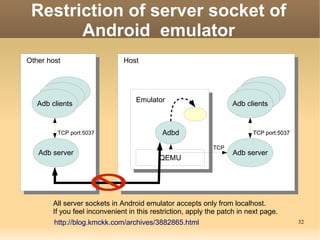
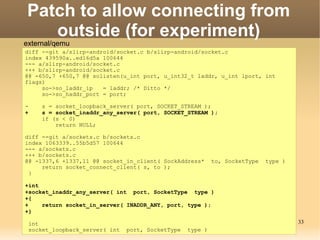
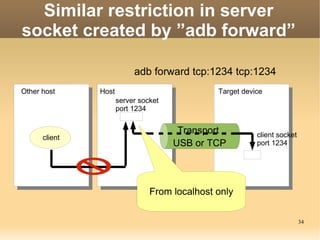
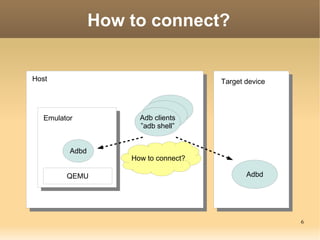
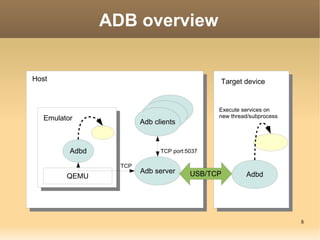
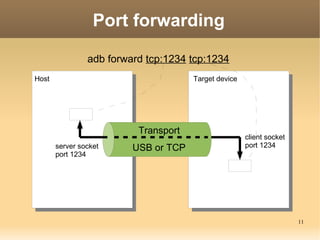
The document discusses the Android Debug Bridge (ADB) and how it works. It provides an overview of ADB including the three main components: ADB clients, server, and daemon (adbd). It also covers topics like command details, tips, advanced features and the internal workings of ADB.








![Source code
system/core/adb in Android source tree
16,000 lines in *.[ch]
From this directory adb and adbd are built
Don't confuse.
common files between adb and adbd
adb.c, fdevent.c, transort.c, transport_local.c,
tansport_usb.c, service.c, sockets.c, util.c
#if ADB_HOST
/* code for adb*/
#else
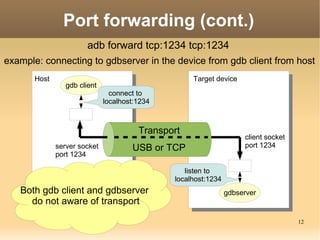
/* code for adbd */
#endif
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ads2012adb-120213170017-phpapp01/85/ADB-Android-Debug-Bridge-How-it-works-14-320.jpg)


![Sequence chart
Adb client
“adb shell ls” Adb server adbd
host:version
OKAY0004001d
Check version
host:transport-any
Specify the OKAY
destination
shell:ls
[OPEN]shell:ls
Command subprocess
to adbd
[OPEN]shell:ls
OKAY
ls
[WRITE]len=247
len=247
stdout len=247
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ads2012adb-120213170017-phpapp01/85/ADB-Android-Debug-Bridge-How-it-works-17-320.jpg)