Init of Android
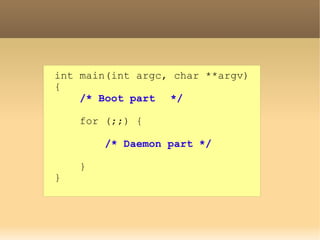
The /init process in Android is different than a typical Linux system. It has two main parts - a boot part and a daemon part. The boot part sets up directories and parses the /init.rc file. The daemon part runs in a forever loop handling events from four file descriptors for devices, properties, signals, and keychords. It is responsible for device management, property updates, restarting services, and special key combinations. The /init process is statically linked so it can run independently of the system.