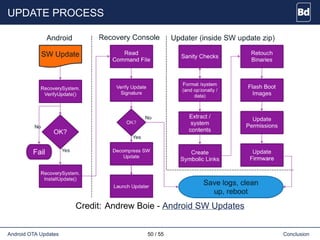
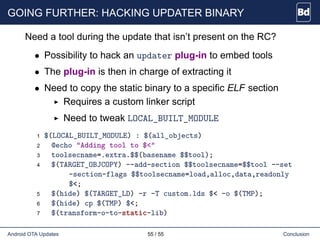
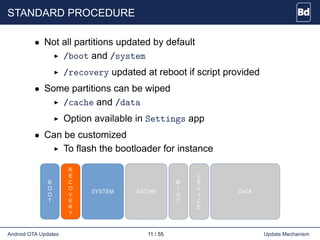
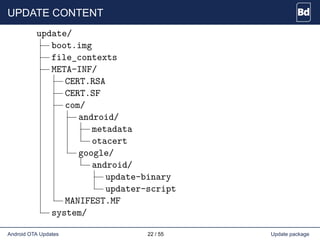
The document discusses Android over-the-air (OTA) updates, including the update mechanism, update packages, and the recovery console. It describes how OTA updates work in Android, from downloading an update package to verifying and applying the updates. It also discusses the AOSP components involved like the updater binary, edify scripting language, and recovery console. Finally, it covers creating an OTA application to check and download updates and rebooting into recovery to apply them.







![OTHER OPTIONS
• Using adb sideload
1 $ adb reboot recovery
2 [Press VOL_UP and SEARCH]
3 [Select 'apply update from ADB']
4 $ adb sideload update.zip
Android OTA Updates 12 / 55 Update Mechanism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidotaupdates-160812082510/85/Android-OTA-updates-12-320.jpg)











![UPDATER PLUG-INS
• plug-in snippet:
1 #include "edify/expr.h"
2
3 Value* CustomImxFn(const char* name, State* state,
4 int argc, Expr* argv[]) {
5 if (argc != 2) {
6 return ErrorAbort(state, "%s expects 2 args", name);
7 }
8 // Do custom work
9 }
10
11 void Register_librecovery_updater_imx() {
12 RegisterFunction("imx_custom", CustomImxFn);
13 }
Android OTA Updates 29 / 55 Update package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidotaupdates-160812082510/85/Android-OTA-updates-29-320.jpg)