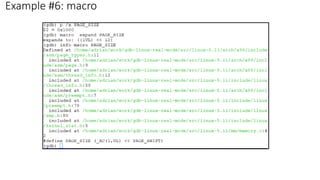
The document provides a detailed guide for setting up and debugging the Linux kernel using qemu and gdb in an x86_64 environment, primarily based on kernel 5.11. It includes instructions for environment preparation, launching the virtual machine, and specific gdb commands for examining kernel data structures. Examples of breakpoints and memory structures are also discussed to aid in understanding the debug process.









![Page Map
Level-4 Table
40
CR3 init_top_pgt = swapper_pg_dir
Sign-extend
Page Map
Level-4 Offset Physical Page Offset
0
30 21
39 20
38 29
47
48
63
Page Directory
Pointer Offset
Page Directory
Offset
Page Directory
Pointer Table
Page Directory
Table
level3_kernel_pgt
PDPTE #511
PDPTE #510 PDE #506
PDE #507
PDE #505
Direct Mapping Region
Kernel Code & fixmap
cpu_entry_area: 0.5TB
vmalloc: 32TB
PDE #13
PML4E #402
PML4E #273
…
PML4E #465
PML4E #468
PML4E #508
PML4E #511
vmemmap (page
descriptor)
PDPTE #0
Page Table Offset
1211
PTE #82 = 0
PTE #83 = 0
Page Table
Physical Memory
page frame
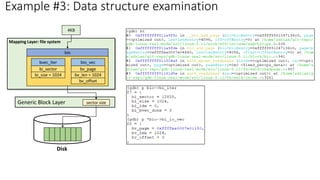
Example #4: Page Table Examination
[Linear Address] 0xffff_c900_01a5_2000, 0xffff_c900_01a5_3000
1
2
3
4
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qemugdb-220826072647-500ee596/85/qemu-gdb-The-efficient-way-to-understand-debug-Linux-kernel-code-data-structure-12-320.jpg)