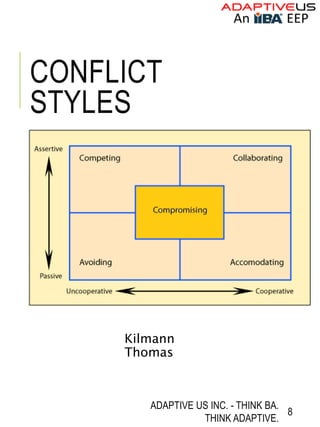
The document discusses the inevitability of conflicts in life and business, emphasizing the importance of managing them effectively through various techniques. It outlines different conflict styles (competing, accommodating, avoiding, compromising, collaborating) and their appropriate contexts, as well as strategies for resolution such as negotiation, compromise, and expert mediation. The role of emotions in conflict management is also highlighted, with tips on how to navigate them constructively.