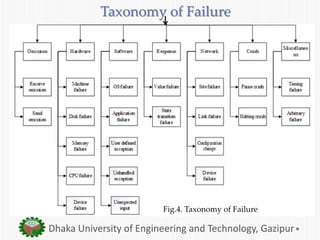
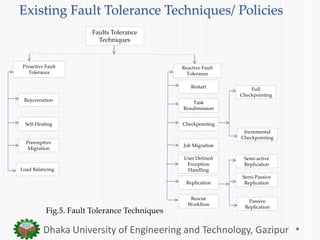
The document presents an overview of fault tolerance techniques in cloud computing. It discusses related work on fault tolerance methodologies. It defines a taxonomy of faults, errors, and failures in cloud computing. It also describes existing proactive and reactive fault tolerance techniques such as checkpointing, replication, and load balancing. Finally, it outlines some developed cloud fault tolerance techniques like a proactive fault tolerance manager and a self-tuning failure detection approach.