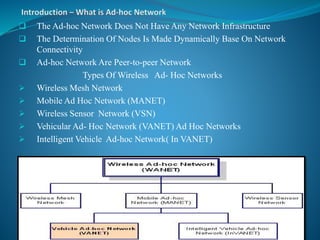
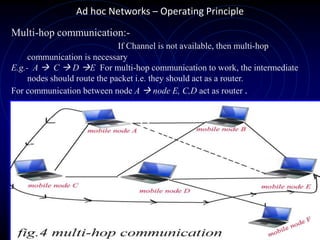
The document provides an overview of ad hoc networks, describing their decentralized nature and operation, including mobile and multi-hop communications. It discusses various types of ad hoc networks and identifies key issues such as network topology changes, scalability, and energy constraints that affect implementation. Applications of ad hoc networks are highlighted, including military use, disaster recovery, and personal device connectivity.