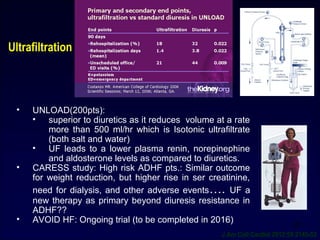
Low dose dopamine increases GFR and RBF. The DAD-HF trial investigated 60 patients randomized to low dose furosemide (continuous infusion 0.5 mg/kg/day) with or without low dose dopamine (2 μg/kg/min). Dopamine preserved renal function compared to furosemide alone in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. There were no significant differences found in a trial comparing high vs low dose furosemide or bolus vs continuous infusion on renal function or symptoms. Novel agents targeting fluid overload, renal function, contractility, and vasomotion may provide new therapeutic options for acute heart failure.

![AHFS : NOT VERIFIED
Similarities and differences between acute MI & AHFS in
hospitalization in the US
Incidence 1 million per year 1 million per year
Mortality
Pre hospitalization
In hospital
After discharge [ 60-90 d]
High
3-4%
2%
?
3-4%
10%
Myocardial injury Yes Likely
Pathophysiological target Clearly defined
[coronary thrombosis]
Uncertain
Clinical benefits of
interventions in published
clinical trial
Beneficial Minimal / no benefit or
deleterious compared with
placebo
ACC / AHA recommendation LEVEL A NONE
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-2-320.jpg)

![Linking Short- term intervention with long-term benefit:
What is needed?
Better understanding of Acute Heart Failure pathophysiology
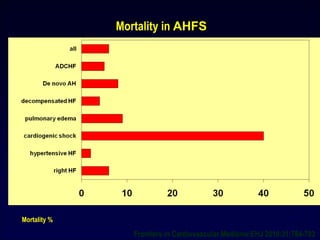
MORTALITY
• Myocardial injury [Tn
release]
• Renal dysfunction [CRS]
• Liver dysfunction
PREVENTION OF END-
ORGAN DAMAGE
Congestion
Viable but
dysfunctional
myocardium
Neurohormonal
& inflammatory
activation
Mechanisms which
can be targeted
Metabolic
factors
Hemodynamic
deterioration
[↑LVFP,↓ CO, ↓ PERFUSION]
Vascular resistance
/stiffness ↑
ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 Reviewed by Ponikowski](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-8-320.jpg)
![BNP Status
This pilot study demonstrates that home BNP testing is feasible and that trials using
home monitoring for guiding therapy are justifiable in high-risk patients. Daily weight
monitoring is complementary to BNP, but BNP changes correspond to larger changes
in risk, both upward and downward. (Heart Failure [HF] Assessment with B-type
Natriuretic Peptide [BNP] In the Home [HABIT]; NCT00946231)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-11-320.jpg)
![Clinical RELEVANCE of promising novel biomarkers(AHFS)
Biomarker Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy guidance Cardiac
Production
NT-proBNP and
BNP
++++ ++++ ++ Solely
Serum Sodium + +++ ++ No
Serum Creatinine - +++ ++ No
MR-proANP +++ ++++ Likely similar to NT-
ProBNP/BNP
Solely
sST2 + ++++ ? Not Exclusively
Hs troponin-I
[EFFECT]
+ ++++ ? Solely
MR-proADM - ++++ ? No
Cystatin C - ++++ ? No
NGAL - ++++ ? No
GDF-15 - +++ ? Not Exclusively
β- Trace protein - +++ ? No
Gal-3 - +++ ? Not exclusively
CRP - ++ ? No
TNF-α - ++ ? No
IL-6 - ++ ? No
PTX3 - ++ ? Unknown
MPO - ++ ? Not exclusively
ET-1 - ++ ? Not exclusively
Copeptin - ++ ? No
PCT ++ ++ ++ No
12
Clinical Chemistry 58:1 127–138 (2012)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-12-320.jpg)



![AHF Treatment Goals
Immediate [ED/ICU/CCU]
•Treat symptoms and restore oxygenation
•Improve hemodynamic and organ
perfusion
•Limit cardiac and renal damage
•Prevent thromboembolism
•Minimize length of ICU stay
Intermediate [in –hospital]
• stabilise pt and optimize treatment
strategy
•Initiate and up-titrate disease modifying
pharmacologic therapy
•Consider device therapy in appropriate
pts
• identify etiology and relevant
comorbidities
Pre-discharge and long term management
•Plan follow up stratergy
•Enroll in ds management programme,
educate and initiate life style adjustments
•Plan to up-titrate / optimise disease
modifying pharmacologic therapy
•Ensure assessed for appropriate device
therapy
•Prevent early readmission
•Improve symptoms
Http://www.Peerviewpress.Com/01/r286](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-19-320.jpg)



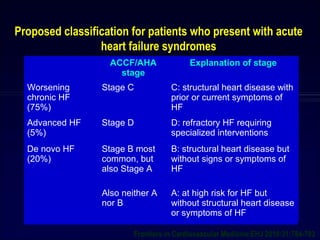
![Short- and long-term novel therapies for AHF syndromes
Short term Long term Both
Levosimendan [LIDO, CASINO, SURVIVE] ? ?
Nesiritide[ ASCEND-HF, ROSE-AHF]
Relaxin [RELAX-AHF]
Myosin Activators Omecamtiv Mecarbil
[ATOMIC-AHF]
RyR2 stabilizers/ rycals
Cinaciguat (UIT)
Adenosine regulating agents
Stresscopin
Istaroxime [HORIZON-HF]
Ularitide [TRUE-AHF, SIRIUS II, URGENT]
Urocrotins [UNICORN]
Hypertonic Saline
Ultrafiltration [RAPID-CHF, UNLOAD]
IABP
EECP [PEECH]
CAFA
IMT
Direct renin
Inhibitors (DRI)
[ASTRONAUT]
Macronutrients
Micronutrients
CRT/AICD
Adenosine Antagonists
[PROTECT, REACH UP rolofylline]
Vasopressin Antagonists
[EVEREST, TACTICS-HF]
Digoxin [DIG]
CD-NP
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine EHJ 2010:31;784-793 modified 2013
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-23-320.jpg)






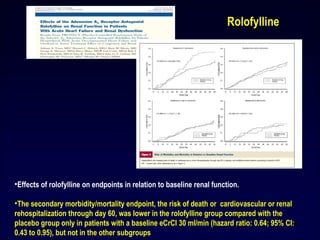

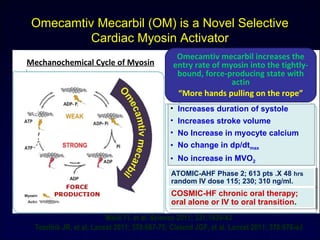
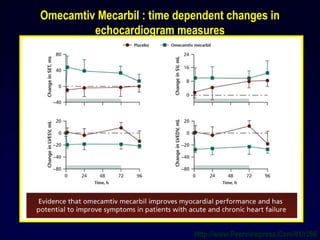
![Levosimendan enhances contractility by increasing responsiveness of myofilaments to calcium. The
cardiac myosin activator Omecamtiv mecarbil stimulates myosin adenosine triphosphatase
(ATPase), thereby increasing force generation. Istaroxime inhibits activity of plasma membrane
sodium-potassium ATPase and increases the activity of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum
calcium ATPase (SERCA).
Mechanism of action of novel contractility-enhancing
medications.
Omecamtiv mecarbil
(Modified from Tavares M, Rezlan E, Vostroknoutova I, et al. New pharmacologic therapies for acute heart failure. Crit Care Med
2008; 36[Suppl]:S112-S120.)
33
Istaroxime
Levosimendan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-33-320.jpg)
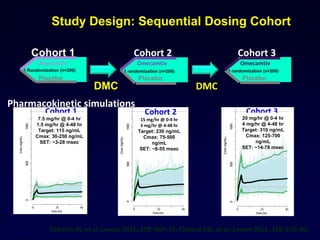
![ATOMIC –AHF Omecamtiv Mecarbil Dyspnea Response
Teerlink J R ESC 2013, Symposium 4503
Response rate
ratio
1.02 1.02 1.41
95% CI [0.74 -1.42] [0.76 – 1.37] [1.02 -1.93]
Response rate ratio : ratio of response rate to placebo with each cohort](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-36-320.jpg)

![• Istaroxime is a novel intravenous agent with inotropic and lusitropic properties
related to inhibition of Na/K adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) and stimulation
of sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase.
• 120 AHF pts and reduced systolic function. Three sequential cohorts of 40
patients each were randomized 3:1 istaroxime:placebo to a continuous 6-h
infusion. The first cohort received 0.5 g/kg/min, the second 1.0 g/kg/min, and the
third 1.5 g/kg/min istaroxime or placebo.
• In patients hospitalized with HF, istaroxime improved PCWP and possibly
diastolic function. In contrast to available inotropes, istaroxime increased SBP
and decreased HR.
Istaroxime
Mihai Gheorghiade et al JACC 2008:03;015
39
[HORIZON-HF Trial]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-39-320.jpg)




![Pre-RELAX-AHF : Rapid dyspnea improvement through
24 hours [Likert Scale]
Teerlink J R Lancet 2009,373:1429-1439](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-45-320.jpg)
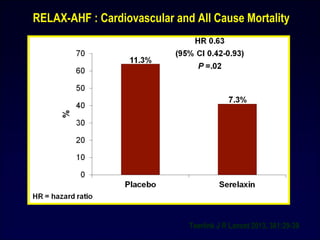
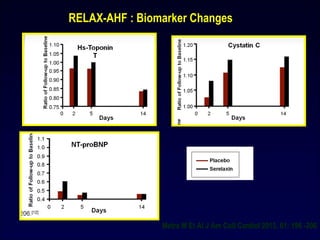
![RELAX-AHF
• 1161 pts with AHF
• 19% improvement in dyspnea
• Decreases in worsening HF
• Improvement of in-hospital signs and symptoms of HF
• Decreased length of hospital stay
• No significant difference in second primary efficacy endpoint of the
proportion of pts with dyspnea relief
• No significant effect on secondary endpoints of cardiovascular death
or hospital readmission for HF or renal failure [RELAX –AF was not
powered as a mortality trial]
Teerlink J R Lancet 2013, 381:29-39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-48-320.jpg)

![• Cinaciguat (BAY 58-2667) is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC, second messenger that internalizes the
message carried by intercellular messengers such as peptide hormones and NO) activator that is
being developed as a first-in-class treatment for acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF). It acts
independently of the sGC ligand nitric oxide.
• Cardioprotective effects in animal models, and pilot clinical studies found that it was well tolerated,
unloaded the heart and increased cardiac output.
• This placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, international phase IIb study
investigated the safety and efficacy of intravenous cinaciguat (per-protocol) as add-on to standard
therapy in 139 patients with ADHF (NYHA functional class III and IV; pulmonary capillary wedge
pressure [PCWP] ≥ 18 mmHg).
• Cinaciguat rapidly and significantly reduced PCWP and PVR and increased cardiac output in patients
with ADHF, without impairing cardiac or renal function. Hypotension occurred in some patients;
further dose titration studies are therefore required to establish the optimal dosing strategy for this
promising new therapy.
Cinaciguat
JACC Mar 9,2010 Vol:55 issue 10A
50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-50-320.jpg)

![• Nesiritide is approved in the United States for early relief of dyspnea in patients with acute
heart failure. Previous meta-analyses have raised questions regarding renal toxicity and the
mortality associated with this agent.
• We randomly assigned 7141 patients [ASCEND-HF trial]
• Co-primary end points were the change in dyspnea at 6 and 24 hours, and the composite end
point of rehospitalization for heart failure or death within 30 days.
• Nesiritide was not associated with an increase or a decrease in the rate of death and
rehospitalization and had a small, nonsignificant effect on dyspnea when used in
combination with other therapies.
• It was not associated with a worsening of renal function, but it was associated with an
increase in rates of hypotension. On the basis of these results, nesiritide cannot be
recommended for routine use in the broad population of patients with acute heart failure.
Nesiritide
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adhfcsi13drucsamal-160203125548/85/Acute-Decompensated-Heart-Failure-53-320.jpg)





