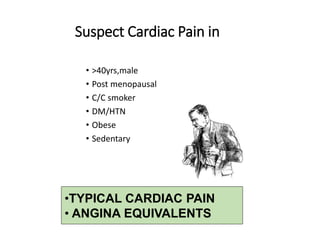
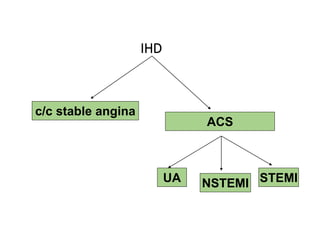
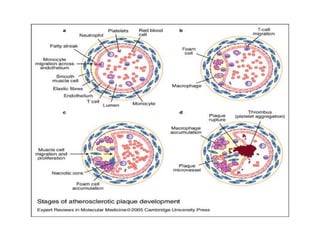
This document discusses the evaluation and management of acute chest pain, which can be caused by conditions like angina, myocardial infarction (MI), or other musculoskeletal and gastrointestinal issues. Key points include:
- Taking a history, examining vital signs, performing an ECG and cardiac biomarkers to determine if the pain is cardiac or non-cardiac in nature.
- For suspected acute coronary syndromes like unstable angina or NSTEMI, treatment involves antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, nitrates, beta blockers and revascularization if needed.
- For STEMI, prompt treatment involves aspirin, clopidogrel, thrombolytics if eligible, and managing any arrhythmias or mechanical complications