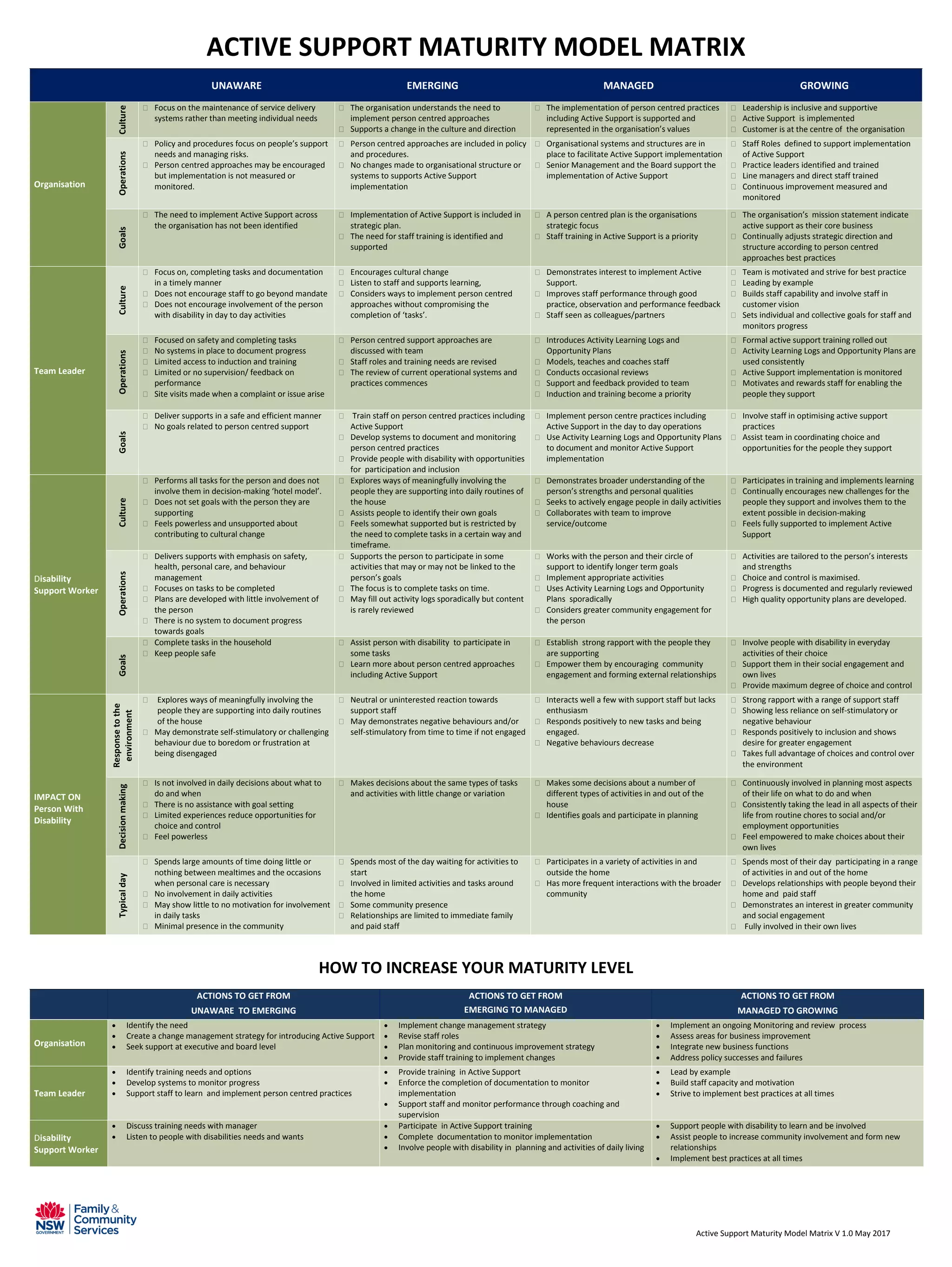
The Active Support Maturity Model Matrix outlines a progression from an unaware organization to one that fully embraces person-centered practices and active support. It emphasizes the importance of cultural change, effective training, and continuous monitoring to prioritize individuals' needs and empower them in decision-making. The document provides actionable steps for organizations to enhance their capacity for implementing active support in a meaningful way.