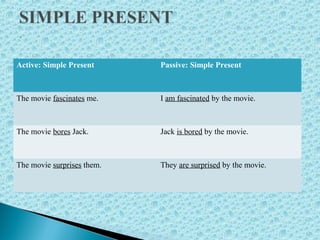
The document discusses the active and passive voice in English grammar. It defines active voice as using the subject of the sentence to express the agent performing the action of the main verb. Passive voice uses the subject to denote the recipient of the action rather than the performer. The passive is formed using an auxiliary verb like "be" or "get" plus the past participle of the main verb. Examples are provided of changing sentences from active to passive voice.