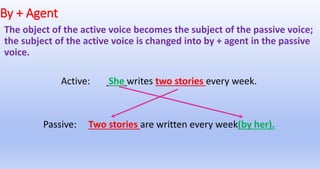
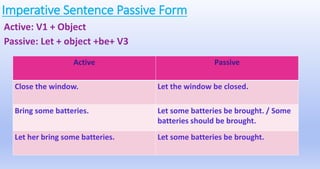
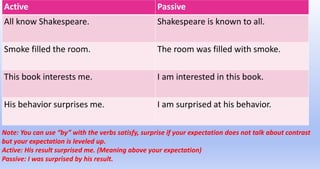
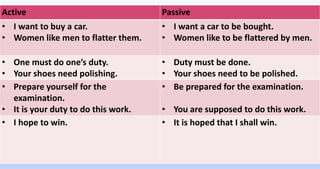
The document explains the concepts of active and passive voice in English grammar, detailing their structures, rules, and usage examples. It emphasizes that in active voice, the subject performs the action, while in passive voice, the subject receives the action, often highlighting the object instead of the doer. Additionally, it outlines the transformation process from active to passive voice and provides guidelines for various tenses and constructions.