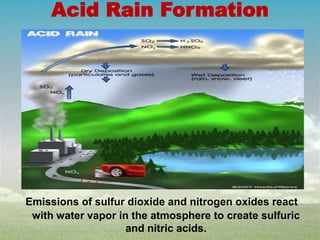
Acid rain is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions reacting with water in the atmosphere to form acids. It has lowered the pH of rainwater below 5.6. The main causes are fossil fuel combustion by power plants, vehicles, and industries. Acid rain harms plants, aquatic animals, soils and buildings. It leaches nutrients from soils and releases aluminum ions toxic to fish. Control measures include using cleaner energy sources, pollution controls on industries and vehicles, and liming of affected lakes and soils.