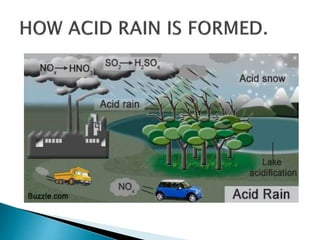
Acid rain is caused by sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides released from the burning of fossil fuels and other industrial processes reacting with water and oxygen in the air to form acids. It falls to earth through both wet deposition like rain, snow, and fog, and dry deposition of gases and particles, damaging both living and non-living things. Acid rain leaches nutrients from soil and water, weakens trees, and harms aquatic ecosystems and wildlife while also posing risks to human health. Efforts are needed to reduce emissions and mitigate the effects of acid rain.